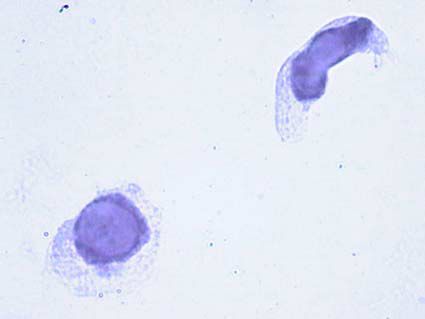
Decoy cells:
A morphologic sign of the (re)activation of polyomaviruses in the kidneys and urothelium of transplanted patients is the detection of typical intranuclear viral inclusion bearing epithelial cells, so-called “decoy cells”, in the urine. The large inclusion sometimes occupies the entire nucleus and gives it a dark gelatinous featureless appearance, due to the homogenization of its content. Some cells have an empty nucleus with a rim of dark dense chromatin clumps, they look alike the mononuclear cells with Herpesvirus cytopathological effects. Because of these pitfalls, never make the diagnosis of “decoy” cells based in only one or few cells. In the early studies, these cells were considered to look like malignant ones, and because of this the “decoy” term was coined. Decoy cells can be confirmed by EM studies, FISH or immunocytochemistry.
“Decoy” means an artificial animal used to lure game, especially ducks.