What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder Diabetes means high blood sugar level in the body. The body cannot make an adequate return to become insulin. Without insulin, our body cannot get energy.
And insulin we get from our bodies is to be found in the pancreas. That allows glucose to enter the body’s cells, where it is used as fuel for energy so we can work, play and generally live our lives. It is vital for life.
Diabetes is a disease in which the body is unable to properly use and store glucose (a form of sugar). And glucose is vital to our health because of its important source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and tissue. and it’s also the main fuel source of our brain.
What is Insulin?
Insulin was discovered in 1921 by Banting. Insulin is a peptide hormone that is exclusively produced by pancreatic beta cells. Beta cells are situated into the pancreas, in clusters known as the islets of Langerhans. Insulin is a small protein.
Insulin is a two-chain polypeptide having 51 amino acids and MW (molecular weight) about 6000. The A-chain has 21 while B-chain has 30 amino acids.
Insulin is a key to open our cells and it permits the glucose to enter and permit to use glucose for energy. while, not insulin, there is no key so the sugar stays in the blood and builds up in the blood. for this reason cells hungry from lack of glucose. if will not treat this so the blood damages the nerve, heart, eye, and kidney and it can also to coma and death.
Insulin is considered to be the main anabolic hormones of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, protein fats, by using promoting the absorption of main glucose from the blood into liver, fat, and skeletal muscles cell.
In this tissue, the absorbed glucose is transformed into both glucogens through glycogenesis or fat through lipogenesis or inside the case of the liver into both. Glucose manufacturing and secretion with the aid of the liver is strongly inhibited by a high concentration of insulin in the blood.
How does Insulin work?
Insulin is hormones and that occupy from the pancreas which is situated behind and below the stomach. Insulin is hormones which are made by our body organ called the pancreas and it helps your body to turn blood sugar into energy. and the insulin is working following method
- After eat you eat the blood sugar rise.
- Then the pancreas secretes insulin into the bloodstream.
- The insulin propagates, enabling sugar to enter your cells.
- Insulin decreases the amount of sugar in your bloodstream.
- As your blood sugar level decreases, so does the secretion of insulin from your pancreas.
Types of Diabetes
1. Type-1 Insulin Depended on Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
2.Type-2 Non-insulin Depended on Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)
1.Type-1 Insulin Depended Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
It’s also called juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus Diabetes, the body completely stops producing any insulin, a hormone that enables the body to use glucose found in foods for energy. This form of diabetes usually develops in children or young adults.
There is beta cell destruction in pancreatic.
2.Type-2 Non-insulin Depended on Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)
It’s also called maturity diabetes mellitus diabetes, the body doesn’t produce enough insulin and is unable to use insulin properly (insulin resistance). His form of diabetes usually occurs in people who are over 40, overweight and have a family history of diabetes, there is no loss or moderate reduction in B cell mass insulin in circulation is low. Over 90% of cases are type 2.
Causes
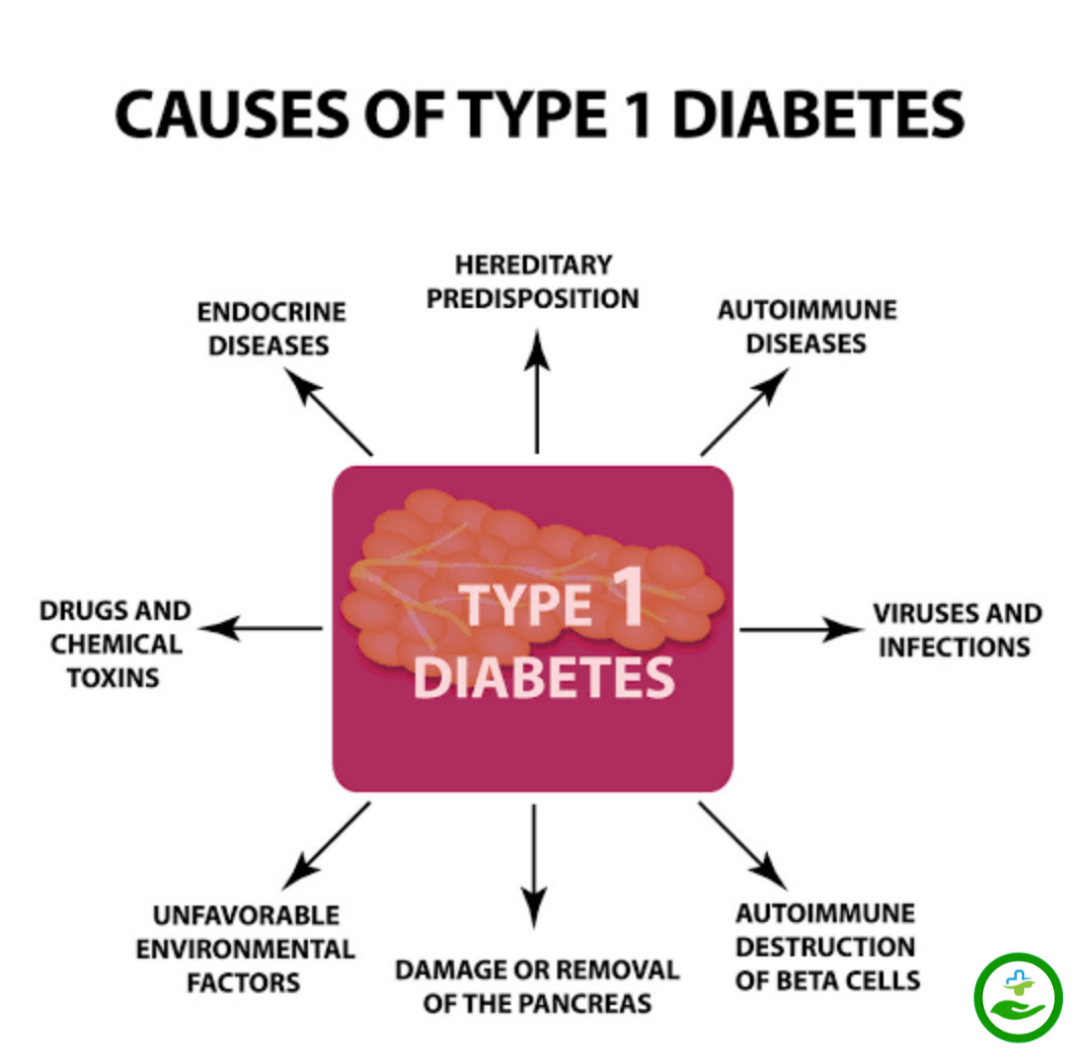
Type -1 Diabetes- Generally there are no specific causes but the following reason involved.
- They cause by the immune system means the immune system by mistake destroying the insulin-making cell in the pancreas.
- Viral or bacterial infection.
- Some chemical toxin.
Type-2 Diabetes- There is much reason to cause type 2 diabetes
- From genetic and lifestyle factor and environmental factor.
- Obesity (Overweight).
- Bad Diet.
Gestational Diabetes ( Causing During Pregnancy)- The causes of diabetes in pregnancy is called Gestational diabetes.there are following factor that increases the causes of gestational diabetes.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Overweight.
- Family history of Gestational Diabetes
Symptoms

- Increased hunger.
- Frequent urination.
- Weight loss.
- Being very thirsty Increased hunger.
- Blurry vision.
- Irritability.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet.
- Frequent skin, bladder or gum infections.
- Wounds that don’t heal.
- Extreme unexplained fatigue.
Diagnosis Test
If anyone has the symptom of this disease so it should be tested. This test is most often used.
![]() Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) -This test measures your blood glucose level.
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) -This test measures your blood glucose level.
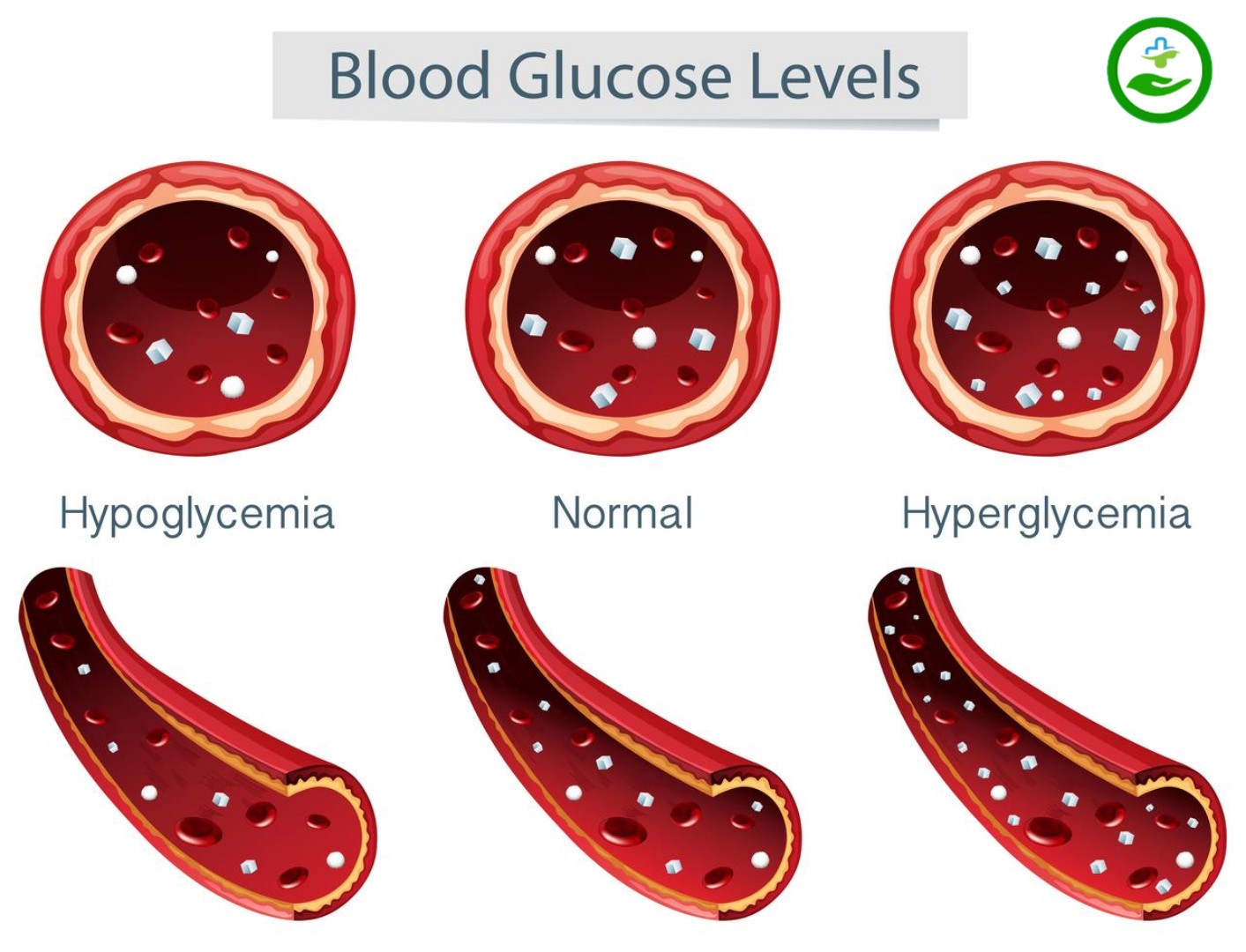
- Fasting (Fasting mean empty stomach means nothing eat or drink except water) blood sugar level less than 100mg/dl is normal.
- A fasting blood sugar level from 100-125mg/dL have Prediabetes.
- Fasting Blood sugar level above 126mg/dL or higher on 2 times tested means you have Diabetes.
![]() Random Blood Sugar Test- This test used in emergency time means in this test, the doctor does not wait for their fasting. If A level of 11.1 mmol/L or more in the blood sample so they indicate diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Test- This test used in emergency time means in this test, the doctor does not wait for their fasting. If A level of 11.1 mmol/L or more in the blood sample so they indicate diabetes.
![]() Oral Glucose Tolerance Test– This test is measure blood glucose level after you fast for at least 8 hours or overnight.then you will dring sugary Liquid. then draw the blood sugar level every 2-3 hours.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test– This test is measure blood glucose level after you fast for at least 8 hours or overnight.then you will dring sugary Liquid. then draw the blood sugar level every 2-3 hours.
- A blood sugar level less then 140mg/dL(7.8/mmol/dL) is normal reading.
- After 2 hours reading is more than 200mg/dL (11.1/mmol/dL). it means they indicate diabetes.
- If reading is 140-199mg/dL (7.8/mmol/dL-11.1/mmol/dL). it means they indicate prediabetis.
Guidelines & Management
Management and control of blood sugar are very important as it prevents or reduces the risk of developing the complications of the disease. The abnormally high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), can cause kidney, eye, heart, blood vessel, and other diseases. The main aim of disease management is to keep the following under control :
- Blood glucose levels
- Blood pressure
- Cholesterol levels
Depending on the type and severity of diabetes :
- With diet plus exercise,
- Diet, exercise, and medication.
- Medication may be insulin injections or tablets, or both.
Management of type 1 diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes is controlled by insulin.
- insulin pump
Management of type 2 diabetes
- Healthy eating
- Regular exercise
- Possibly, diabetes medication or insulin therapy
- Blood sugar monitoring
Treatment & Medicines
Type-1 Diabetes
In this condition pancreas, cant produce insulin to control blood sugar naturally.so you need to take insulin for managing your blood sugar. Insulin injection is main medication of type-1 diabetes.in this condition, you will need daily insulin injection to maintain your blood glucose level.
Insulin injection available in four different forms, and they all working slightly differently.they all differentiated by their work.
- Long-Acting -Insulin starts to work within a few hours and its work up to 24 hours.
- Short-Acting -Insulin starts to work within a 30 minutes and it works up to 6-8 hours.
- Intermediate -acting-Insulin starts to work within 1 hour and it works up to 12-18 hours.
- Rapid-acting -They work starts within 15 minutes and works up to 3-4 hours.
Type-2 Diabetes
-
Metformin. -It works by improving the sensitivity of your body tissues to insulin so that your body uses insulin more effectively.
-
Sulfonylureas – These medications help your body secrete more insulin. Examples of medications in this class include glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase), glipizide (Glucotrol) and glimepiride (Amaryl). Possible side effects include low blood sugar and weight gain.
-
Meglitinides. These medications work like sulfonylurea by encouraging the body to secrete more insulin, but they’re faster acting, and they don’t stay active in the body for as long. They also have a risk of causing low blood sugar, but not as much risk as sulfonylurea do. Weight gain is a possibility with this class of medications as well. Examples include repaglinide (Prandin) and nateglinide (Starlix).
-
Thiazolidinediones- Like metformin, these medications make the body’s tissues more sensitive to insulin. This class of medications has been linked to weight gain and other more serious side effects, such as an increased risk of heart failure and fractures. Because of these risks, these medications generally aren’t the first-choice treatment. Rosiglitazone and pioglitazone are examples of thiazolidinediones.