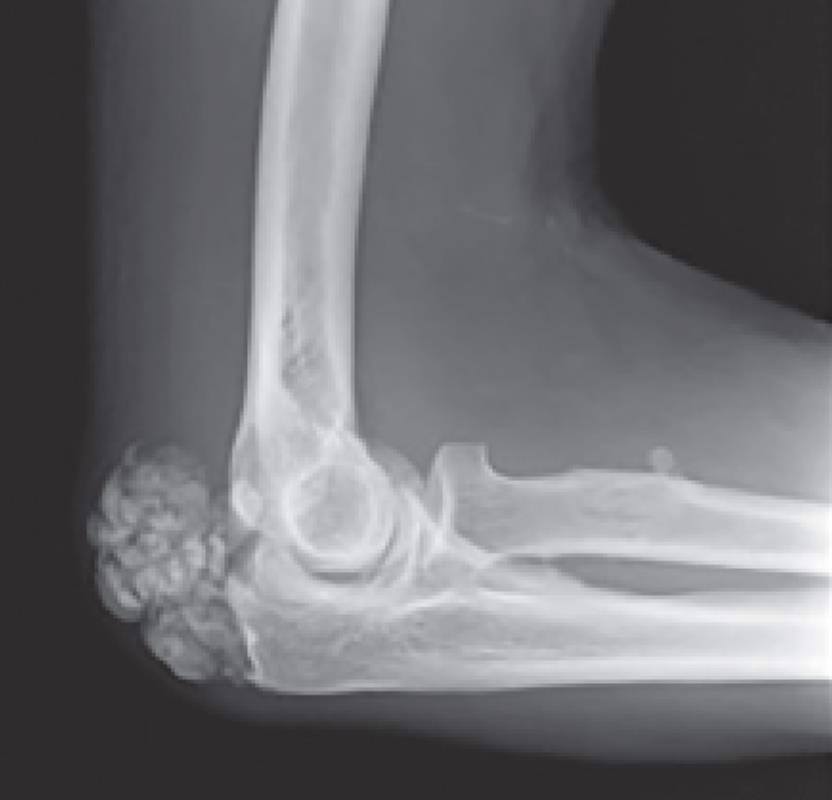
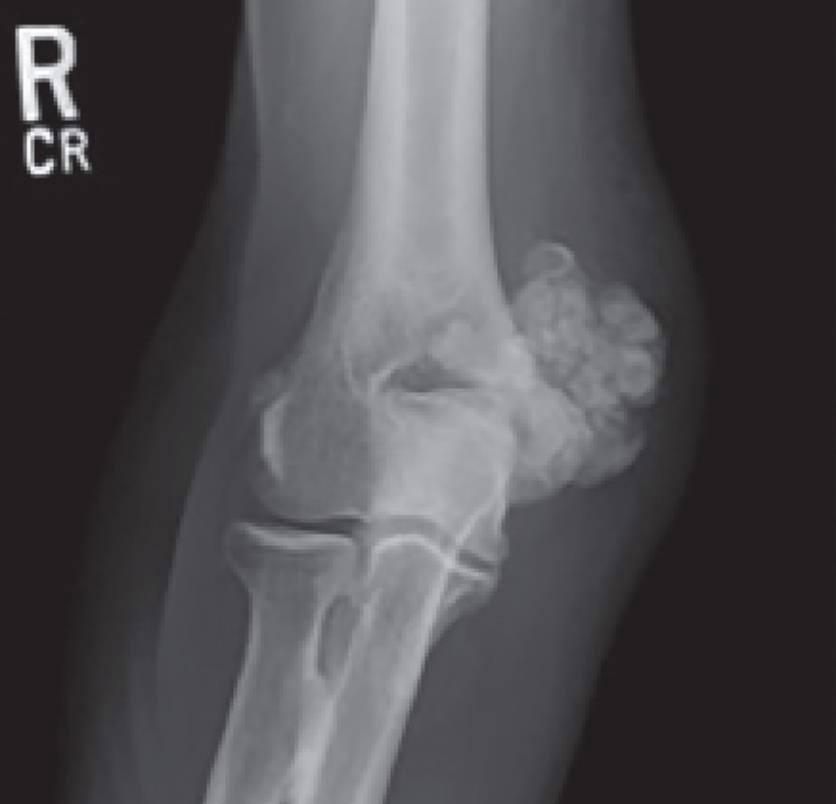
Tumoral calcinosis is the pathologic deposition of calcium adjacent to joints and occurs in the presence of phosphate dysregulation. Commonly associated syndromes include familial hyperphosphatemic tumoral calcinosis and calcinosis of renal failure. The genetic defect of the FGF-23 gene leads to hyperphosphatemic tumoral calcinosis. Laboratory findings are often significant for hyperphosphatemia but may be associated with elevated PTH, uric acid, and alkaline phosphatase. Calcinosis usually involves the hip and the shoulder. Treatment involves normalizing serum phosphate and surgical removal of symptomatic lesions.