Q-1. An infant presents with 15-20 watery stools since 9 days. Along with Zinc, what else should be given to the patient?
a) ORS alone
b) ORS and low lactose feed
c) ORS with antibiotics
d) ORS with probiotics
Answer: ORS alone
Explanation:
ORS is fluid of choice in most patients with mild to moderate dehydration.
Oral zinc should be given to speedy recovery and decrease the risk of future diarrheal episodes.
Important point:
Viral diarrhoea: Vomiting, low grade fever and voluminous watery diarrhoea and usually lasts 4-8 days
Oral rehydration fluid is appropriate in most cases of diarrhoea of viral origin.
Q-2. 3.5 kg newborn born by term normal delivery presented with respiratory distress not responding to surfactant therapy. There is also a history of female sibling death at 1 month due to respiratory distress. Diagnosis:
a) RDS due to surfactant deficiency
b) Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
c) Meconium aspiration syndrome
d) Diaphragmatic palsy
Answer: Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Explanation:
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis:
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is rare familial disease caused by congenital surfactant protein B deficiency.
It manifests severe and lethal respiratory distress syndrome in term and near tern infants.
Characterized by alveolar filling with granular, eosinophilic material that stains positive using the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) method
It is not responded with exogenous surfactant therapy in fatal cases.
Q-3. A child with fever and barky cough presented to emergency at 3 am. His respiratory rate is 36/min, stridor only on coughing, fever 39 degrees Celsius. No other abnormality, what is the next logical step?
a) Dexamethasone
b) Racemized epinephrine
c) Do nothing, just reassure
d) Give surfactant
Answer: Dexamethasone
Explanation:
Croup syndrome:
Acute inflammatory disease of the larynx including viral croup (Laryngo-tracheo-bronchitis), epiglottitis and bacterial tracheitis.
Viral croup (Laryngo-tracheo-bronchitis):
Caused by para-influenza virus (Most common), RSV, influenza, rubeola, adenovirus and Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Clinical findings:
Barking cough
Stridor
Low grade fever or absent fever
Cyanosis in severe cases
Treatment viral croup:
Oral hydration
Oxygen administration
Nebulize racemic epinephrine solution/ Budesonide inhalation
Single dose dexamethasone (0.6 mg/Kg) improves symptoms and decreased hospitalization
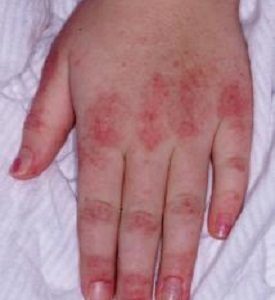
Q-4. 9 yr girl present with difficulty in combing, climbing stairs and erythematous lesion at MCP joint. Gower sign is positive. What is the next step for diagnosis?
a) CK level
b) Rheumatoid factor
c) Electromyography
d) Nerve conduction studies
Answer: Electromyography
Explanation:
Juvenile dermato-myositis is a systemic, autoimmune inflammatory muscle disorder and vasculopathy.
Characteristic findings include Gottron papules, a heliotrope rash, calcinosis cutis, and symmetrical, proximal muscle weakness.
Diagnosis of Juvenile dermato-myositis:
Muscle enzyme levels in blood- Elevated
MRI of weak muscles may show disease activity even when enzymes are normal.
Electromyography is useful for distinguishing Myopathic from neuropathic causes.
Muscle biopsy is indicated in doubtful cases.
Important point:
Gowers’ sign indicates weakness of the proximal muscles, namely those of the lower limb.
Gottron papules are present over the metacarpophalangeal joints and proximal interphalangeal joints in a child with juvenile dermatomyositis.
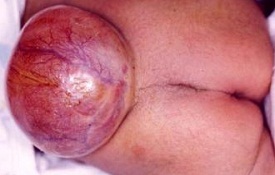
Q-5. Congenital defect seen in this baby:
a) Cranio-rachischisis
b) Meningocele
c) Myelo-meningocele
d) Spina bifida occulta
Answer: Myelo-meningocele
Explanation:
The lumbar region of a newborn baby with Myelomeningocele: The skin is intact, and the placode-containing remnants of nervous tissue can be observed in the center of the lesion, which is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Myelomeningocele results from failed closure of the caudal end of the neural tube, resulting in an open lesion or sac that contains dysplastic spinal cord, nerve roots, meninges, vertebral bodies, and skin.
Myelomeningocele most commonly involves lumbo-sacral region.
Important point:
Patients with myelo-meningocele present with lower limb paralysis and sensory loss, bladder and bowel dysfunction, and cognitive dysfunction.
Q-6. While assessing a child for malnutrition, all are criteria except:
a) Mid arm circumstances
b) Edema
c) Weight for height
d) Height for age
Answer: Height for age
Explanation:
Criteria for assessing a child for malnutrition:
Weight for height
Bipedal edema of nutritional origin
Mid arm circumstances
Visible severe wasting
Q-7. Pervasive developmental disorder associated with all except-
a) Repetitive behavior
b) Impaired communication
c) Impaired language
d) Impaired cognition
Answer: Impaired cognition
Explanation:
Pervasive developmental disorder denotes a group of disorders with the common findings of impairment of socialization skills and characteristic behavioral abnormalities.
Speech and language deficits are common as well.
Q-8. Earliest sign of puberty in females is-
a) Growth spurt
b) Breast budding
c) Thelarche
d) Menarche
Answer: Thelarche
Explanation:
Thelarche or breast development (1-11 years) is usually the first sign of puberty in females.
Growth of the testes and thinning of scrotum (11-12 years) is the first sign of puberty in males.
Q-9. Milk is deficient in?
a) Iron and Vit C
b) Iron and Vit A
c) Phosphorus and Vit C
d) Phosphorus and Vit A
Answer: Iron and Vit C
Explanation:
Cow milk deficient in:
Vit D
Vit C
Iron
Human milk deficient in:
Vit D
Thiamin
Iron
Important point:
Human milk contains sufficient amount of Vit C but deficient in thiamin.
Q-10. What is the diagnostic test you would do for a P2L2 pregnant female at 18 weeks of gestation having a history of 1 baby with thalassemia?
a) CVS
b) NIPT
c) Amniocentesis
d) Cordocentesis
Answer: Cordocentesis
Explanation:
Prenatal diagnosis for genetic disorders: Sampling
Chorionic villus sampling: Carried out after 11 weeks gestation to obtain DNA for analysis
Amniocentesis: Done after 16 weeks
Fetal blood sampling (Cordocentesis): Carried out at 18 weeks or more gestation