Therapy of iron overload cardiomyopathy:
Dietary interventions to minimize or eliminate iron ingestion are not feasible or useful.
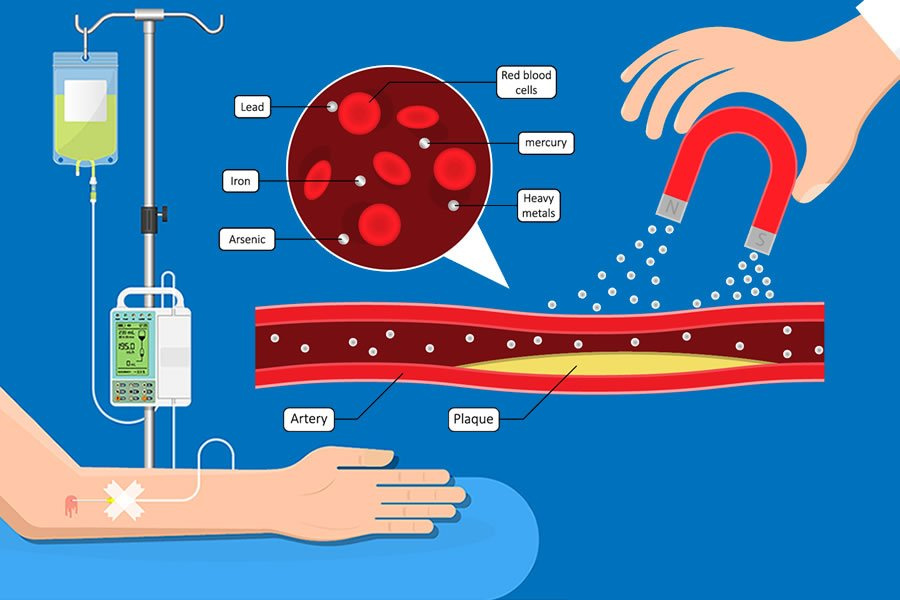
Phlebotomy removes 400–500 mL of blood (200–250 mg of iron) at each session, thus mobilizing iron from the organs where it is stored for the production of haemoglobin. Early in the disease, this procedure is done up to 1–2 times a week to obtain a target ferritin below 20 ng/mL, and then maintenance phlebotomy is performed 2–4 times a year.
Chelation therapy is used in patients not suitable for required phlebotomy, such as those with significant anaemia or malignancy. It removes iron by binding to it and then excreting the compound in urine and bile. Presently available chelators include deferoxamine (subcutaneous or IV) and oral deferiprone.