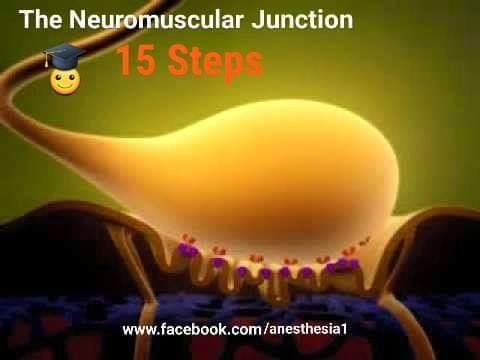
THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION
15 basic steps
- The action potential arrives at the NEURO-MUSCULAR junction.
- Calcium enters the presynaptic nerve terminal
- Magnesium moves out
- The Acetylcholine laden vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane
- Acetylcholine is released then into the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction through exocytosis
- 2 Acetylcholine molecules bind to the NICOTINIC Acetylcholine receptor
- At least 25-30% binding is needed
- An END PLATE POTENTIAL is generated which moves across the sarcolemma and percolates the muscle cell through the T-tubule
- The DIHYDROPYRIDINE receptor on the T-tubule then STIMULATES the RYANODINE receptor on the intracellular SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM
- The CALCIUM is then released from the SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM and moves into the SARCOMERE
- It unlocks the TROPOMYOSIN cable from ACTIN exposing the active subunit
- The MYOSIN head is simultaneously charged into position by ATP
- MYOSIN binds to ACTIN
- CONTRACTION OCCURS
- The MUSCLE SHORTENS
DrJoosab
(aka DrRoc)