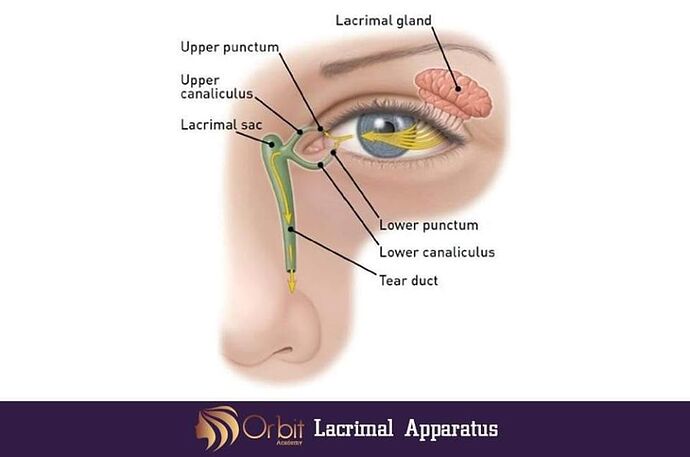
There are different surgical techniques available for DCR. Transcanalicular laser-assisted DCR (TLDCR) is the most recent DCR technique.
TLDCR is a minimally invasive surgical technique. It has lower morbidity than external DCR.
Advantages of transcanalicular laser-assisted endoscopic DCR compared with conventional external DCR include the following:
- minimal or no postoperative ecchymosis, edema or inflammation.
- less surgical manipulation of medial canthal tissues and lacrimal pump
- no scarring on the skin
- minimal intra- and postoperative bleeding
- faster recovery time
- the laser is directed away from the orbit so there is less risk of injury
- it is considerably faster than the external DCR
- easy to learn
- usually done under local anaesthesia.
In comparison with nonlaser endoscopic techniques, transcanalicular laser-assisted endoscopic DCR has the advantage of minimal bleeding and requires less complex endoscopic skills.
The procedure is usually performed in patients who are concerned about external scarring and want a minimally invasive procedure. In addition, it is advantageous for patients who have bleeding disorders or must remain on anticoagulation medication.
Equipment
An endoscopic tower with a rigid endoscope is required. A number of different lasers have been used to perform transcanalicular endoscopic DCR, including argon, erbium (Er):YAG, neodymium (Nd):YAG, and, most recently, the diode laser.
Endoscopic DCR is contraindicated in patients who have lacrimal or nasal sinus neoplasia.
Relative contraindications include dacryolithiasis, canalicular obstruction, and canaliculitis. In addition, caution is needed in patients with altered nasal anatomy.