Q-141. Most common presenting feature of Asherman’s syndrome is
a) Oligomenorrhoea
b) Hypomenorrhoea
c) Menometrorrhagia
d) Dysmenorrhoea
Answer: Hypomenorrhoea
Explanation:
Asherman syndrome, also known as uterine synechiae, is a condition characterized by formation of intrauterine adhesions.
Common presenting feature of Asherman’s syndrome:
Infertility
Pregnancy loss
Menstrual abnormalities such as pypo-menorrhoea
Abdominal pain
Important point:
Gold standard investigation- Direct visualization of uterine cavity by Hysteroscopy
Q-142. Folic acid to be started with anticonvulsants-
a) As soon as pregnancy is confirmed
b) One month before pregnancy
c) After delivery
d) All females with a possibility of getting pregnant
Answer: All females with a possibility of getting pregnant
Explanation:
Because many pregnancies are unplanned, folic acid supplementation is given routinely to all women (On anti-epileptic medications) of childbearing potential at 0.4 mg/day to prevent neural tube defects.
Q-143. Levo- norgesterol is not use for
a) Endometriosis
b) Premenstrual tension
c) Emergency contraceptive
d) Atypical hyperplasia
Answer: Premenstrual tension
Explanation:
Indications of Levo- norgesterol:
Emergency contraception
Endometriosis
Endometrial hyperplasia
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Q-144. Post coital contraceptives are all except
a) IUD
b) LNG
c) Desogestrel
d) Ulipristal
Answer: Desogestrel
Explanation:
Emergency contraception or post-coital contraception:
Copper-bearing intrauterine devices (IUDs)
Emergency contraception pills (ECPs) – Levo-norgestrel and Ulipristal acetate
Combined oral contraceptive pills or the Yuzpe method-The Yuzpe method
Q-145. Most probable cause for beaded appearance of fallopian tube & club bing of fimbriae on HSG is:
a) Mycoplasma hominis
b) Candida
c) Tuberculosis
d) Chlamydia
Answer: Tuberculosis
Explanation:
Female genital tuberculosis remains as a major cause of tubal obstruction leading to infertility, especially in developing countries.
Hystero-salpingographic presentation of tubal TB vary from non-specific changes such as hydro-salpinx to specific pattern such as “beaded tube”, “golf club tube”, “pipe-stem tube”, “cobble stone tube” and the “leopard skin tube”
Q-146. Estrogen and progesterone production in first two months of pregnancy is by
a) Ovary
b) Placenta
c) Adrenal glands
d) Corpus luteum
Answer: Corpus luteum
Explanation:
In the luteal phase following ovulation, estrogen and progesterone are secreted by the corpus luteum, which forms through the action of luteinizing hormone (LH).
The corpus luteum continues to be the source for estrogen and progesterone in early pregnancy.
During early pregnancy, growth of the corpus luteum is stimulated by chorionic gonadotropin (CG), a peptide hormone that is synthesized by the trophoblast after the embryo implants.
CG is an LH analogue, thus it binds to the LH receptor, maintaining the corpus luteum in an active state throughout the first three months of pregnancy.
Starting at about the third month of pregnancy, the placenta takes over as the source of estrogen and progesterone.
Q-147. Smallest AP diameter
a) Obstetric conjugate
b) Diagonal conjugate
c) Inter-spinous diameter
d) Traverse
Answer: Obstetric conjugate
Explanation:
The true conjugate can be measured only on radiographic films because it extends from the sacral promontory to the top of the symphysis pubis. Its normal measurement is 11 cm or more.
The obstetric conjugate is the shortest of the three. It extends from the sacral promontory to the thickest part of the pubic bone and measures 10 cm or more.
The diagonal conjugate is the most easily and commonly assessed because it extends from the lower border of the symphysis pubis to the sacral promontory. It normally measures 11.5 cm or more.
Q-148. Menopause is diagnosed by
a) FSH> 40IU/L
b) Estradiol <30 IU/L
c) Progesterone < 15IU/L d) LH<40IU/L Answer: FSH> 40IU/L
Explanation:
Menopause may now be more precisely defined as amenorrhea with signs of hypo-estrogenemia and an elevated serum FSH level of greater than 40 IU/L.
Important point:
The diagnosis of menopause is confirmed by follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) levels >40 IU/L.
Q-11. 23 year old female presented with pruritus and discharge in genital area. Cervical smear shows the following image. Diagnosis is
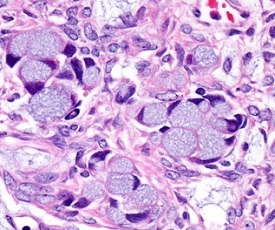
a) Klebsiella granulomatosis
b) Gardnerella
c) Trichomonas
d) Chlamydia
Answer: Gardnerella
Explanation:
Image shows “clue cells”, sloughed epithelial cells coated with Gram-variable pleomorphic cocco-bacilli.
Q-12. Hysteroscopic finding in 52 year old lady complaining of post menopausal bleeding as in image
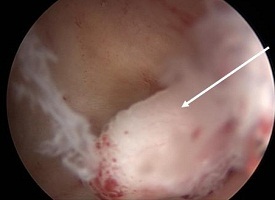
a) Endometrial polyp
b) TB endometrium
c) Fibroid
d) Endometrioma
Answer: Endometrial polyp
Explanation:
Hysteroscopic finding suggests a growth from the mucosa of endometrial cavity suggestive of endometrial polyp.
Hysteroscopy may be used to either diagnose or treat uterine polyps.