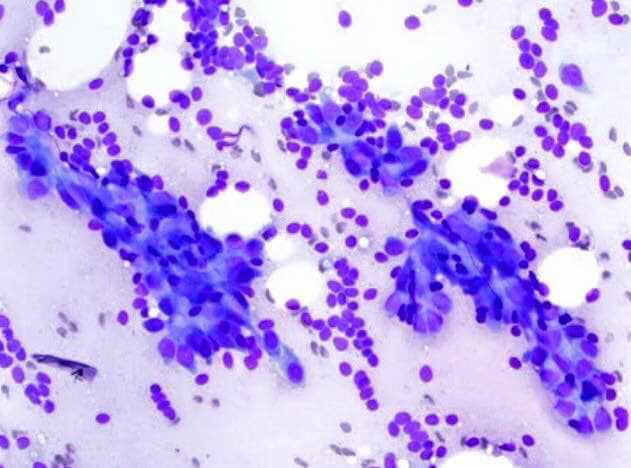
FIBROADENOMA
------'------------------------
● diagnostic findings on needle biopsy consist of :
a) abundant stromal cells which appear as bare bipolar nuclei.
b) sheets of fairly uniform-size epithelial cells that are typically arranged in either an antler-like pattern or a honeycomb pattern.
c) Foam cells and apocrine cells may also be seen, although these are less diagnostic features.
• Fibroadenoma of the breast is a benign tumor composed of two elements: epithelium and stroma.
• It is nodular and encapsulated, included in breast.
• epithelial proliferation —appears in a single terminal ductal unit and describes duct-like spaces surrounded by a fibroblastic stroma.
• Depending on the proportion and the relationship between these two components, there are two main histological features:
A) Intracanalicular fibroadenoma :
● stromal proliferation predominates and compresses the ducts, which are irregular, reduced to slits.
 Pericanalicular fibroadenoma :
Pericanalicular fibroadenoma :
● fibrous stroma proliferates around the ductal spaces, so that they remain round or oval, on cross section.
The basement membrane is intact .
■ NOTE :-
-------------’
● tightly arranged ductal epithelial cells with dyscohesive bare nuclei ( s/o fibroadenoma)
■Features that are suggestive of malignancy :-
a) include loss of cell cohesion,
b) increase in cell and/or nuclear size
c) irregularity of the nuclear membrane
d) clumping and uneven distribution of chromatin,as well multiple, abnormal nucleoli.
e) Single nucleoli may be seen in reactive conditions and are not a criterion of malignancy on their own.
f) Myoepithelial cells, which are abundant in benign proliferative lesions, are not seen in aspirates of invasive breast carcinoma