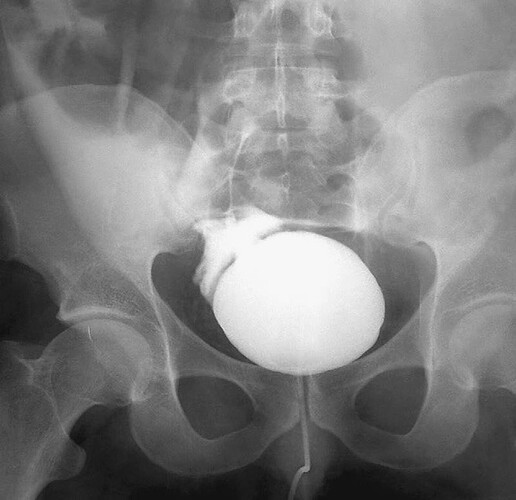
INTRAPERITONEAL BLADDER RUPTURE
===================================
Typically, the dome ruptures after a full bladder has sustained blunt force, with subsequent urine extravasation into the peritoneal cavity. Gross hematuria may or may not be present. In standard cystography, at least 250 mL of 30% iodinated contrast material is instilled into the bladder via a Foley catheter. In male patients, urethral injury must first be excluded. Scout, full bladder, and postvoid anteroposterior views of the pelvis are obtained. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture is diagnosed by the presence of contrast material within the peritoneal cavity. Contrast material will be seen outlining loops of bowel and layering in the peritoneal recesses.