Normal Pap smear cells:
¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤¤
-
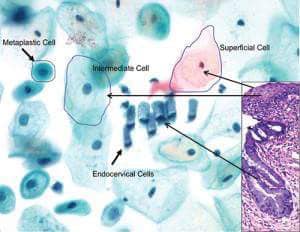
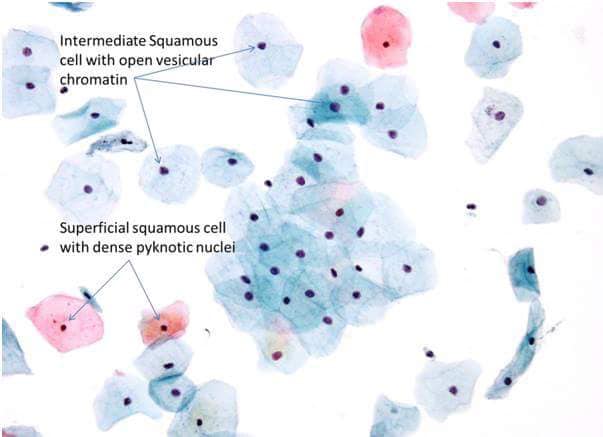
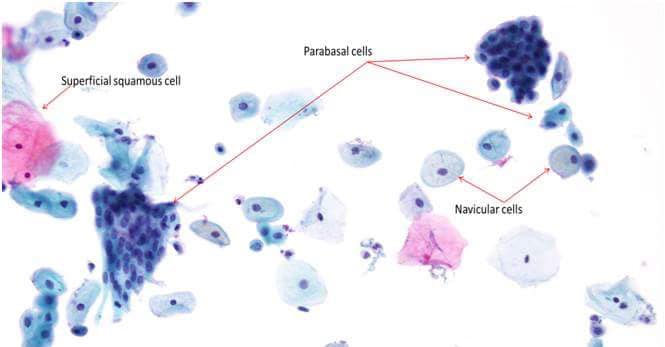
#Superficial Squamous Cells:-
☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
● The superficial squamous cell comprises the outermost layer of the non-keratinizing epithelium.
● Eosinophillic polygonal shaped cell with centrally placed pyknotic nucleus.
● No nuclear detail can be seen due to nuclear degeneration.
● Superficial squamous cells are seen in abundance during late proliferative andovulatory phases of the menstrual cycle.
● Superficial Squamous Cells are seen in abundance when estrogen is at High levels.
-
#Intermediate Squamous Cells:
☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
● Polygonal-shaped intermediate squamous cells found in the stratum spongiosum (midzone) layer of the squamous epithelium.
● The intermediate cell’s cytoplasm is thin, transparent, and typically stains basophilic (Bluish) with centrally placed nucleus.
● Nucleus is vesicular with fine evenly dispersed granular chromatin.
● Intermediate squames are seen in abundance when progesterone is at high levels.
● This occurs during the luteal and early follicular phases of the menstrual cycle, and the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
-
#Parabasal Squamous Cells:-
☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
● Parabasal squamous cells are found in the basal layer of the squamous epithelium.
● They are smallest epithelial cells seen on a typical vaginal smear.
● They are round- to oval-shaped cell with dense homogenous basophilic cytoplasm encloses a nucleus with finely granular chromatin.
● Parabasals are an uncommon finding on Pap smears of women with estrogen production or replacement hormone.
● These cells are often seen in patients who lack estrogen, including those who are premenstrual, post partum, taking estrogen-restricting hormones, or postmenopausal.
-
#Squamous Metaplastic Cells:
☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
● Squamous metaplastic cells are round to polygonal in shape with dense biphasic staining cytoplasm and round centrally located nuclei.
● They arise from the basal layer of glandular epithelium as a protective response to stimuli, creating the transformation zone.
●These metabolically active cells are often the site where abnormalities occur.
● Throughout a woman’s lifetime, the transformation zone regresses from the ectocervix and up into the endocervical canal.
-
#Navicular cells:-
☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
● It represent a variant of intermediate cells.
● Often seen in pregnancy or post-partum.
● The cells are ‘boat’ shaped with a thickened outer rim of cyanophilic/eosinophilic cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei.
● Central cytoplasmic brown/yellow staining indicates glycogen production.
● Navicular cells are seen with high progesterone levels when superficial squamous cells exfoliate more readily: thus they may be seen with progesterone-only contraceptive use.