On this page:
Thenar MusclesHypothenar MusclesLumbricals MusclesInterossei Muscles
Hand muscles: The muscles of the hand are responsible for the hand and fingers movement. The muscles of the hand are redivided into two groups: the extrinsic muscles and the intrinsic muscle groups. The extrinsic groups are the long flexors and extensors muscles. They are termed extrinsic muscles because the muscle belly is positioned on the forearm. The intrinsic muscles located within the hand itself. The hand muscles are innervated by the radial, median, and the ulnar nerves.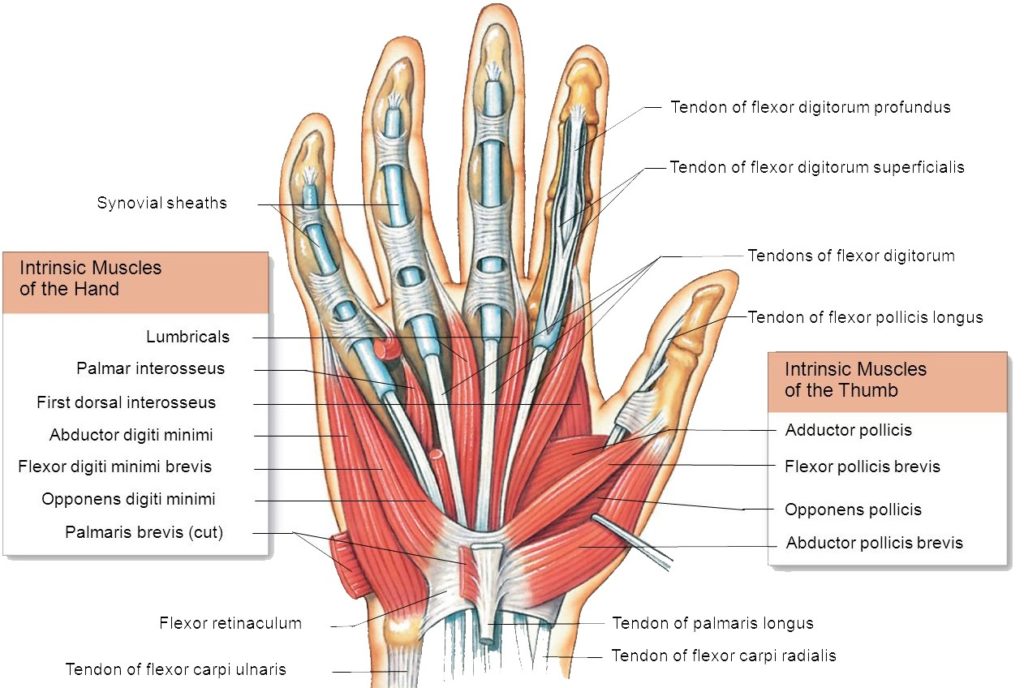
Thenar Muscles
The three thenar muscles are the short muscles positioned at the base of the thumb. The thenar hand muscles are liable for the fine movements of the thumb.
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis: The abductor pollicis brevis is a hand muscle that works as an abductor of the thumb.
Origin: Tubercle of scaphoid, trapezium, flexor retinaculum.
Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Action: Abduction of thumb.
Nerve Supply: Median nerve.
Flexor pollicis brevis: The flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
Origin: Flexor retinaculum, trapezoid and capitate bones
Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Action: Flexes metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb.
Nerve Supply: Median nerve. The deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis is supplied by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve.
Opponens pollicis brevis: The opponens pollicis is a triangular small muscle in the hand, which act to oppose the thumb. It is lying deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis muscles.
Origin: Flexor retinaculum.
Insertion: Shaft of metacarpal bone of the thumb.
Action: Pulls thumb medially and forward across the palm.
Nerve Supply: Median nerve.
Hypothenar Muscles
The hypothenar muscles are of four short muscles located at the ulnar side of the palm. The hypothenar hand muscles control the motion of the little finger.
Palmaris brevis
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digiti minimi
Opponens digiti minimi
Abductor digiti minimi: The abductor digiti minimi muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. Its chief role is to pull the little finger apart from the other fingers.
Origin: Pisiform bone.
Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx of the little finger.
Action: Abducts the little finger.
Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve.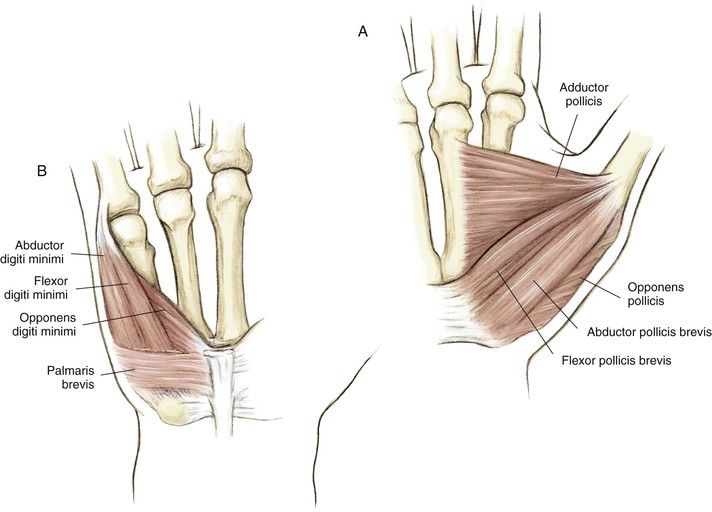
Flexor digiti minimi: The flexor digiti minimi brevis flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. It is located lateral to the abductor digiti minimi during the hand is in anatomical position.
Origin: Flexor retinaculum.
Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx of the little finger.
Action: Flexes the MCP joint of the little finger.
Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve.
Opponens digiti minimi: The opponens digiti minimi is a triangular form and placed immediately under the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and the flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of the muscles that control the little finger.
Origin: Flexor retinaculum
Insertion: Medial border of the 5th metacarpal bone
Action: Pulls 5th metacarpal forward as in cupping the palm
Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve.
Palmaris Brevis: Palmaris Brevis is small, thin muscle, found superficially in the subcutaneous tissue of the hypothenar eminence.
Origin: Originates from the palmar aponeurosis and the flexor retinaculum.
Insertion: Palmaris Brevis inserted into the dermis of the skin on the medial margin of the hand.
Function: Ridges the skin of the hypothenar eminence and develops the curvature of the hand, enhancing the hand grip.
Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve
Lumbricals Muscles
The four lumbricals hand muscles in the hand, each is associated with the finger movement. Lumbricals muscles are very crucial to finger movement, joining the extensor tendons to the flexor tendons.
Origin:
1st – lateral side of the tendon of 2nd digit
2nd – lateral side of the tendon of the 3rd digit
3rd – adjacent sides of the tendon of 3rd and 4th digits
4th –adjacent sides of the tendon of 4th and 5th digits
Insertion:
All are inserted via extensor expansion into the dorsum of bases of distal phalanges.
Function: The lumbricals muscles flex at the MCP joint, and extend at the interphalangeal (IP) joints of the individual finger.
Nerve Supply: The medial two lumbricals (little and ring fingers) are supplied by the ulnar nerve. The lateral two lumbricals (index and middle fingers) are supplied by the median nerve.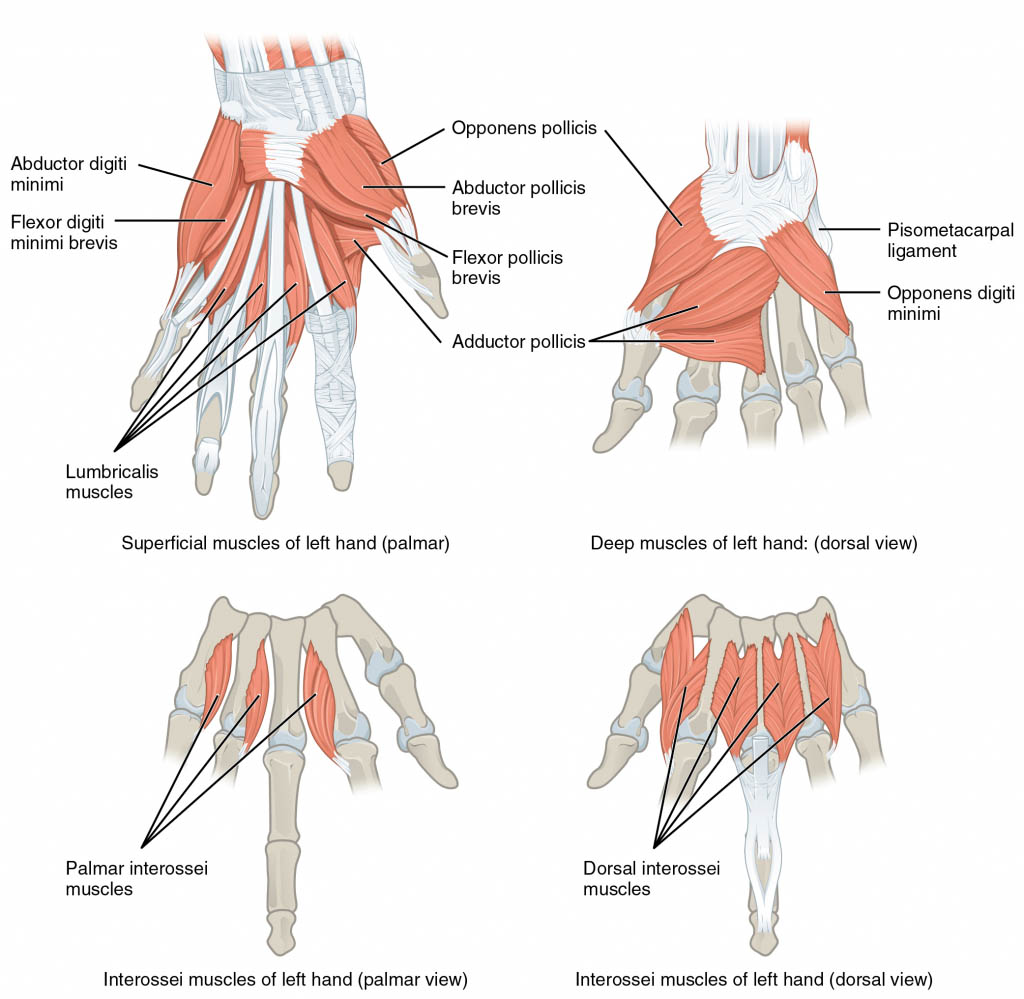
Interossei Muscles
The interosseous hand muscles are found near the metacarpal bones which serve to control the fingers movement. The interosseous muscles lie in the interosseous spaces within the metacarpal bones. They are voluntary muscles. They are usually divided into two groups-palmar and dorsal.
Palmar Interossei: Palmar interossei are four small, unipennate muscles in the hand that lie within the metacarpal bones and are connected to the index, ring, and little fingers. The Palmar interossei are smaller than the dorsal interossei muscles of the hand.
Origin:
1st: medial side of the base of 1st metacarpal
2nd: medial side of 2nd metacarpal
3rd: lateral side of 4th metacarpal
4th: lateral side of 5th metacarpal
Insertion:
1st – medial side of the base of proximal phalanx of thumb or 1st digit
2nd, 3rd, 4th – via extensor expansion into the dorsum of bases of distal phalanges of 2nd, 4th, and 5th digits.
Function: Abduct the fingers at the MCP joint.
Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve.
Dorsal Interossei: Dorsal interossei are four muscles in the back of the hand that work to abduct the index, middle, and ring fingers apart from hand’s midline and assists in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension through the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and the ring fingers.
Origin:
1st – adjacent sides of 1st and 2nd metacarpals
2nd – adjacent sides of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals
3rd – adjacent sides of 3rd and 4th metacarpals
4th – adjacent sides of 4th and 5th metacarpals
Insertion :
All are inserted via extensor expansion into the dorsum of bases of distal phalanges of 2nd, 3rd, and 4th digits
Function: Adducts the fingers at the MCP joint.
Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve.
One adductor of thumb muscles is adductor pollicis
Adductor pollicis:
Origin:
Oblique head: bases of 2nd -3rd metacarpals
Transverse head: shaft of 3rd metacarpal
Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Action: Adduction of thumb.
Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve.
Tags :