Diseases under surveillance as per International Health Regulations are:
Cholera
Yellow Fever
Plague
Mnemonic (acronym): CYP (as in Cytochrome P450) is notifiable.
Visual mnemonic: Child Playing with a Yellow ball.

Ornithodoros kelleyi – soft tick
Mnemonic for diseases spread by soft tick is: Soft Relapse of Q fever at KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken)
Expansion of the mnemonic:
Soft – Soft tick
Relapse – Relapsing fever
Q fever – Q fever
KFC – Kyasanur Forest Disease

Mnemonic for names of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI’s):
FFPSEC – Fresh Frozen Plasma Sale and Exchange Company
Fresh – Fluoxetine
Frozen – Fluvoxamine
Plasma – Paroxetine
Sale – Sertraline
Exchange – Escitalopram
Company – Citalopram
Scanning electron micrograph showing sickle cells in the midst of normal RBC’s
Sickle cell anaemia is a condition in which the red blood cells assume an abnormal rigid sickle shape
There is decrease in flexibility of the red cells, which impair their ability to flow freely through blood capillaries
It can result in conditions like vaso occlusive crisis, splenic sequestration crisis, aplastic crisis, haemolytic crisis
It is an autosomal recessive condition
Sickle cell anaemia – Mnemonic
Sickle cell anaemia occurs due to the replacement of hydrophilic amino acid glutamic acid with hydrophobic amino acid valine at the 6th position of the beta globin chain of haemoglobin
The inclusion of the hydrophobic ( non polar ) amino acid promotes non covalent polymerisation of haemoglobin resulting in distortion of the RBC’s into a sickle shape
So, how to remember the amino acids involved?
Just remember this memory key – The Villain replaced the Good guy
The Villain is Valine
The Good guy is Glutamic acid
So you will in turn remember that Valine replaces Glutamic acid
Mnemonic for sequence of changes in Raynaud’s phenomenon: PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
PCR Mnemonic stands for
P – Pallor (Stage of local syncope – extremity becomes pale)
C – Cyanosis (Stage of local asphyxia – extremity becomes cyanosed)
R – Redness (Stage of recovery – extremity turns red)

He-man
Mnemonic for components of Papez circuit: ‘He-Man Ate a Cat’
He – Hippocampus (limbic system)
Man – Mamillary body (hypothalamus)
Ate – Anterior Thalamic Nucleus (thalamus)
Cat – Cingulate gyrus (limbic system)
Note – He-Man is a cartoon character.
Alternate mnemonic: MATCH
Mammilary body
Anterior Thalamic Nucleus
Cingulate gyrus
Hippocampus)
Mnemonic for causes of secondary amyloidosis is : ARTHROSCOPE
A – Ankylosing spondylitis; Arthritis – rheumatic and psoriatic
R – Renal cell carcinoma
T – Tuberculosis
H – Hodgkin’s disease
R – Reiter’s syndrome
O – Osteomyelitis
S – Sjogren’s syndrome
C – Chronic infections
O – Others (bronchiectasis, leprosy)
P – Paraplegia with infection
E – Enteritis – regional
Mnemonic for Day of appearance of rash in a febrile patient is : Very Sick Person Must Take Double Tablets
Very – Varicella (day 1)
Sick – Scarlet fever (day 2)
Person – Pox – small pox (day 3)
Must – Measles (day 4)
Take – Typhus (day 5)
Double – Dengue (day 6)
Tablets – Typhoid (day 7)
Mnemonic for Structures passing through foramen ovale of skull is : OVALE
OVALE stands for:
O – Otic ganglion (Does not pass through it, but lies inferior to it)
V – V3 cranial nerve
A – Accessory meningeal artery
L – Lesser petrosal nerve
E – Emissary vein
MEDIAN TRAP:
Myxoedema
Edema premenstrually
Diabetes
Idiopathic
Acromegaly
Neoplasm
Trauma
Rheumatoid arthritis
Amyloidosis
Pregnancy
Mnemonic 2 – TRAMP:
T – Trauma (occupational)
R – Rheumatiod arthritis
A – Acromegaly
M – Myxoedema
P – Pregnancy
Mnemonic 3: ARMPIT
A – Acromegaly
R – Rheumatiod arthritis
M – Myxoedema
P – Pregnancy
I – Idiopathic
T – Trauma (occupational)
Mnemonic for the branches of the coeliac arterial trunk is : Left Hand Side (LHS)
Left Hand Side stands for:
Left – Left gastric artery
Hand – Hepatic artery
Side – Splenic artery
Mnemonic for clinical features of Bell’s palsy is: BELL’S Palsy
B – Blink reflex abnormal
E – Earache
L – Lacrimation [deficient, excess]
L – Loss of taste
S – Sudden onset
Palsy of VII nerve muscles
Mnemonic for the nerves supplying the scalp is: GLASS
GLASS stands for:
G – Greater occipital/ Greater auricular
L – Lesser occipital
A – Auriculotemporal
S – Supratrochlear
S – Supraorbital
Mnemonic for Proximal attachment (origin) of deltoid muscle is : CLASP
CLASP stands for:
CL – Clavicle (anterior fibers of deltoid arise from the anterior border and superior surface of lateral third of clavicle)
A – Acromion (middle fibers of deltoid arise from the lateral border of acromion process of scapula)
SP – Spine of the scapula (posterior fibers of deltoid arise from the posterior border of spine of scapula)
Note : The fibers of the deltoid converge and is inserted into the deltoid tuberosity of humerus.
Mnemonic for Deep branches of Femoral artery is : “Put My Leg Down Please”
It stands for:
Put – Profundus femoris (deep femoral artery)
My – Medial circumflex femoral artery
Leg – Lateral circumflex femoral artery
Down – Descending genicular arteries
Please – Perforating arteries
Mnemonic for the names and order of arrangement of carpal bones is : ‘She Looks Too Pretty, Try To Catch Her ‘
The arrangement of carpal bones from lateral to medial is: (Proximal row followed by distal row)
She – Scaphoid
Looks – Lunate
Too – Triquetral
Pretty – Pisiform
Try – Trapezium
To – Trapezoid
Catch – Capitate
Her – Hamate
Mnemonic for tributaries of External jugular vein is : PAST
PAST stands for :
P – Posterior external jugular vein
A – Anterior jugular vein
S – Suprascapular vein
T – Transverse cervical vein
Mnemonic for layers of scrotum is “Some Dangerous Englishmen Call It Testis” or “Some Dirty Englishmen Called It Testis”
The layers of scrotum from superficial to deep are:
S – Skin
D – Dartos
E – External spermatic fascia
C- Cremasteric fascia
I – Internal spermatic fascia
Testis
Mnemonic for contents of broad ligament is : BROAD
B – Bundle (ovarian neurovascular bundle)
R – Round ligament
O – Ovarian ligament
A – Artefacts (vestigial structures)
D – Duct (oviduct)
Mnemonic for contraindications for use of lignocaine with adrenaline is : Digital PEN
Digital PEN stands for:
D – Digits (Fingers and toes)
P – Penis
E – Ear
N – Nose tip
Mnemonic for Components of optimal preparation for securing the airway in anesthesia is : SOAP
SOAP stands for:
S – Suction
O – Oxygen
A – Airway
P – Pharmacology
Mnemonic for individuals at high risk for respiratory complications of anesthesia is : COUPLES
COUPLES stands for:
C – COPD
O – Obese
U – Upper abdominal surgery
P – Prolonged bed rest
L – Long surgery
E – Elderly
S – Smokers
Mnemonic for characteristic features of halothane is : HALOTHANE
H- malignant Hyperthermia
A- Anaesthesia without analgesia
L- decomposed by Light
O- vasOdilatOr, brOnchOdilatOr, uterine relaxtant
TH- Thymol as preservtive
A- Amber bottle to store it
N- hepatic Necrosis
E- eraser, Erodes rubber
Mnemonic for causes of failed intubation is : INTUBATION
Infections of larynx
Neck mobility abnormalites
Teeth abnormalties(loose tooth,protuberant tooth)
Upper airway abnormalties (strictures or swellings)
Bull neck deformities
Ankylosing spondylitis
Trauma/tumour
Inexperience
Oedema of upper airway
Narrowing of lower airway
Mnemonic for muscles forming erector spinae is : I Long for Spinach
From lateral to medial, the muscles forming erector spinae are:
Illiocostalis
Longissimus
Spinalis
Mnemonic for drugs used in treatment for ventricular tachycardia : LAMB
L – Lidocaine
A – Amiodarone
M – Mexiletine / Magnesium
B – Beta-blocker
Mnemonic for differential diagnosis of low set ears is DDT
D – Digeorge syndrome
D – Down’s syndrome
T – Turner’s syndrome
Mnemonic for anaesthetic agents used in day care anesthesia is : Indian MAP
Indian – Isoflurane
M – Mivacurium
A – Alfentanil
P – Propofol
Mnemonic for anaesthetic agents causing increased CSF pressure : SNAKE
S – Sevoflurane
N – Nitrous Oxide
A – Althesin
K – Ketamine
E – Enflurane
Mnemonic for causes of renal papillary necrosis is : SODA
S – Sickle cell anaemia
O – Obstruction
D – Diabetes mellitus
A – Analgesic nephropathy
Medical mnemonic for drugs causing pseudomembraneous enterocolitis is : TALC
T – Tetracycline
A – Ampicillin
L – Lincomycin
C – Clindamycin
Mnemonic for factors causing shift of oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve to right : CADET
C – CO2
A – Acid
D – 2,3-DGP
E – Exercise
T – Temperature
Medical mnemonic for Side effects of antipsychotics is : SHADE
S – Sedation
H – Hypotension
A – Anticholinergic
D – Dermatological SEs
E – Endocrine, Extrapyramidal
Medical mnemonic for Features of AIDS Dementia Complex is : AIDS
A – Atrophy of cortex
I – Infection/ Inflammation
D – Demyelination
S – Six months death
Medical mnemonic for types of shock is : SHOCK
S – Septic / Spinal
H – Hypovolemic
O – Obstructive
C – Cardiogenic
K – anaphylactic (K as in lactic)
Medical mnemonic for Spinal cord disorders is : VIBRATED SPASMS
V – Vascular
I – Infection
B – Vitamin B12 deficiency
R – Radiation
A –
T – Tumour / Tauma / Toxins
E – Epidural abcess / Electricity
D – Developmental and hereditary
S – Spondylosis and spine
P – Paraneoplastic
A – Arachinoditis
S – Syringomyelia
M – Multiple sclerosis
S – Systemic disorders
Medical mnemonic for Tools for intubation is : MD SOLES
M Monitor
D Drugs
S Suction
O Oxygen
L Laryngoscope
E ETT
S Syringe/Stylet
Medical mnemonic for Difficult Ventilation is BONES
B Beard
O Obesity/Obsteritisc
N No teeth
E Elderly
S Sleep Apnoea
Mnemonic for features of Argyll Robertson Pupil: ARP
ARP stands for:
Accommodation Reflex Present (read forwards)
Pupillary Reflex Absent (read in reverse)
Mnemonic for differential diagnosis of poor breath sounds after intubation is: DOPE
DOPE stands for:
Displaced tube
Obstruction
Pneumothorax
Esophageal intubation
Mnemonic for drugs that can be given via endotracheal tube are:
ALADIN
A – Atropine
L – Lignocaine
A – Adrenaline
D – Diazepam
I – Isoprenaline
N – Naloxone
Anesthetic agents used for spinal anesthesia – Mnemonic
Little Boys Prefer Toys
Lidocaine
Bupivacaine
Procaine
Tetracaine
Asherman syndrome – Features – Mnemonic
ASHERMAN:
Acquired Anomaly
Secondary to Surgery
Hysteroscopy confirms diagnosis
Endometrial damage/ Eugonadotropic
Repeated uterine trauma
Missed Menses
Adhesions
Normal estrogen and progesterone
Causes of microcytic anemia – Mnemonic – TAILS
It stands for:
Thalassemia
Anemia of chronic disease
Iron deficiency anemia
Lead poisoning
Sideroblastic anemia
The mnemonic for rememering the names of the essential amino acids:
Look There, Look There, VIP Man
The essential amino acids are:
Leucine
Threonine
Lysine
Tryptophan
Valine
Isoleucine
Phenylalanine
Methionine
Some other amino acids are considered to be essential under certain conditions.
The mnemonic for remembering the components of the auditory pathway:
SLIMA
8th nerve
Cochlear nucleus
Superior olivary complex
Lateral lemniscus
Inferior colliculus
Medial geniculate body
Auditory Cortex (Brodmann’s area 41)
The first 2 components are not included in this mnemonic. Just remember that the auditory pathway starts with the auditory nerve, goes to its nucleus (cochlear nucleus) and then suddenly turns into slime (visualise this) – SLIMA.
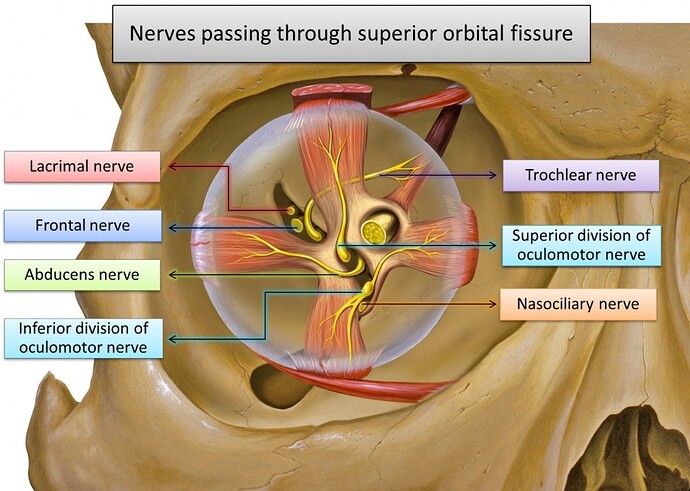
Click on image for an enlarged view
Based on illustration created by Patrick J. Lynch
Mnemonic – “Live Frankly To See Absolutely No Insult”
The nerves passing through superior orbital fissure are (from top to bottom) :
Lacrimal nerve
Frontal nerve
Trochlear nerve
Superior division of oculomotor nerve
Abducens nerve
Nasociliary nerve (branch of ophthalmic nerve)
Inferior division of oculomotor nerve
Differential diagnosis is the systematic method by which diseases of similar presentation are distinguished by considering their various features. VINDICATE is mnemonic which helps to remember the various types of diseases to be considered in a differential diagnosis. VINDICATE stands for
V – Vascular
I – Inflammatory
N – Neoplastic
D – Degenerative / Deficiency
I – Idiopathic, Intoxication
C – Congenital
A – Autoimmune / Allergic
T – Traumatic
E – Endocrine
Menmonic – Very Sick People Must Take Double Tablets
This is decoded as follows:
Fever with rash appearing on (approximately)
Day 1 – Varicella
Day 2 – Scarlet Fever
Day 3 – Small Pox
Day 4 – Measles
Day 5 – Typhus
Day 6 – Dengue
Day 7 – Typhoid