Most common site of origin of vestibular schwannoma is?
A. Cochlear nerve
B. Superior vestibular nerve
C. Inferior vestibular nerve
D. Facial nerve
Correct answer : B. Superior vestibular nerve
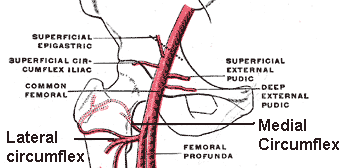
Arteries around the hip joint
Blood supply to head and neck of femur is mainly from?
A. Superficial epigastric artery
B. Medial circumflex femoral artery
C. Lateral circumflex femoral artery
D. Artery of ligamentum teres
Correct answer : B. Medial circumflex femoral artery
Blood supply to head and neck of femur
The blood supply to the head and neck of femur comes from:
Extracapsular arterial ring located at the base of neck of femur
Artery of ligamentum teres
Epiphyseal arteries
Metaphyseal arteries
The extracapsular arterial ring is formed by:
Posteriorly by branches of medial circumflex femoral artery (major part of blood supply)
Anteriorly by branches of lateral circumflex femoral artery
Smaller branches from superior and inferior gluteal artery
Both medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries are branches of profunda femoris artery.
Artery of ligamentum teres
It is a branch of obturator artery.
It contributes a small but variable amount of blood supply.
Pain pathway from ethmoid sinus is via?
A. Nasociliary nerve
B. Lacrimal nerve
C. Lateral pterygoid nerve
D. Frontal nerve
Correct answer : A. Nasociliary nerve
Pain sensation from the ethmoid sinus is transmitted by the anterior and posterior ethmoidal branches of the nasociliary nerve, which in turn is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic division).
The other branches of the nasociliary nerve are:
Long ciliary nerves
Infratrochlear nerve
Communicating branch to the ciliary ganglion (long root of the ciliary ganglion)
Frontal nerve carries sensations from the forehead, frontal sinus mucosa, and the upper eyelid. It has 2 branches – supraorbital nerve and supratrochlear nerve.
Lacrimal nerve innervates the lacrimal gland, conjunctiva, and the lateral upper eyelids.
Lateral pterygoid nerve supplies the lateral pterygoid muscle.
Diplopia in superior oblique palsy is?
A. Vertical diplopia on downward gaze
B. Vertical diplopia on upward gaze
C. Horizontal diplopia on inward gaze
D. Horizontal diplopia on outward gaze
Correct answer : A. Vertical diplopia on downward gaze
Diplopia in superior oblique palsy
In paralysis of the superior oblique muscle (trochlear nerve palsy), maximum diplopia is experienced when the patient looks down.
This is especially important when the patient tries to climb downstairs and when trying to read a book.
The patient tries to compensate by tucking the chin towards the chest.
Weight gain in pregnancy depends on all except?
A. Smoking
B. Pre pregnancy weight
C. Ethnicity
D. Maternal age
Correct answer : A. Smoking
Factors influencing weight gain in pregnancy
Maternal age – Increased weight gain in younger women
Physical activity – Several studies have demonstrated an inverse relation between weight gain and level of physical activity
Prepregnancy weight – Weight gain in pregnancy is generally inversely proportional to BMI (Body Mass Index) in the pre pregnancy period
Race / ethnicity – The mean weight gain differs in various ethnic / racial groups
Parity – Lower weight gain was noted in multipara
Hormonal milieu – Levels of hormones like insulin and leptin can influence weight gain in pregnancy
Multiple pregnancy – Tend to gain more weight in multiple pregnancy
Hyperemesis gravidarum – Lower weight gain in women with hyperemesis gravidarum
Anorexia nervosa – Lower weight gain and lower birth weight in anorexic women
Substance abuse – Studies have found no significant difference in mean weight gain between smoking and non smoking women. But the birth weight was lower in babies born to women who were smokers.
Family violence – Greater risk of inadequate weight gain
Marital status – Many studies have found that married women were more likely to gain weight than single / divorced women
Ref: Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines, Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines; Rasmussen KM, Yaktine AL, Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2009.
Which of the following congenital malformations can be diagnosed in the first trimester ?
A. Microcephaly
B. Anencephaly
C. Meningocele
D. Encephalocele
Correct answer : B. Anencephaly
Congenital malformations diagnosed in the first trimester
Routine ultrasound scan for the diagnosis of congenital anomalies is done in the second trimester
But in high risk cases, an early anomaly scan is done to identify major anomalies
The congenital anomalies that can be identified in the first trimester are:
Acrania – Condition in which the flat bones of the cranial vault are partially or completely absent. It is an early stage of anencephaly.
Exencephaly – An early stage of anencephaly in which the brain is located outside the skull
Anencephaly – Absence of a major part of the brain, skull and scalp. It is an anomaly that occurs when the rostral end of the neural tube fails to close.
A 12 year old Boy with hematemesis, melena and mild splenomegaly presented to the paediatrics OPD. Examination revealed absence of jaundice / ascites. Most probable diagnosis is?
A. Extrahepatic Portal Venous Obstruction (EHPVO)
B. Cirrhosis
C. Non Cirrhotic Portal Fibrosis (NCPF)
D. Malaria with disseminated intravascular coagulation
Correct answer : A. Extrahepatic Portal Venous Obstruction (EHPVO)
Hematemesis, melena and splenomegaly are suggestive of a diagnosis of portal hypertension
The first three options can cause portal hypertension
But considering the age and sex of the child, Extrahepatic Portal Venous Obstruction (EHPVO) is the most probable diagnosis
Non Cirrhotic Portal Fibrosis (NCPF) is usually seen in adult females in the third or fourth decade
Cirrhosis is not very common in children, and it is usually accompanied by jaundice / ascites
A sewage worker with fever and jaundice presented to the emergency department. Lab investigations revealed increased blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine – indicative of renal failure. Which of the following antibiotics is preferred in this patient?
A. Erythromycin
B. Doxycycline
C. Penicillin G
D. Ciprofloxacin
Correct answer : C. Penicillin G
The history of fever and jaundice in a sewage worker with features of renal failure is suggestive of Weil’s disease
Intravenous penicillin G is the preferred antibiotic for treatment of Weil’s disease
Erythromycin can be used as an alternative
In mild cases of leptospirosis, oral therapy with ampicillin / tetracycline is given
Doxycycline is used for prophylaxis against leptospirosis
Sparrow’s foot marks are characteristic of?
A. Vitriolage
B. Windshield glass injury
C. Lightning strike
D. Stab injury
Correct answer : B. Windshield glass injury
Sparrow’s foot marks
They are bizarre lacerations of the face seen in front seat occupants of a vehicle after a road traffic accident
The injury is caused by the shattered windshield glass striking the face of the occupant
Which of the following does not have polysaccharide capsule related antigen antibody response?
A. Haemophilus influenzae
B. Neisseria meningitidis
C. Streptococcus pneumoniae
D. Bordetella pertussis
Correct answer : D. Bordetella pertussis
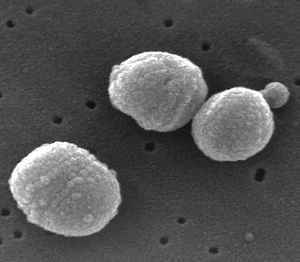
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Scanning Electron Micrograph of Streptococcus pneumoniae showing polysaccharide capsule
Polysaccharide capsule related antigen antibody response
Polysaccharide capsule in an important virulence factor in many organisms like:
Haemophilus influenzae
Neisseria meningitidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Salmonella typhi
Antibodies against the capsule protect against infection
The capsule can be used for producing conjugate polysaccharide vaccines (for H. influenzae, N. meningitidis and S. pneumoniae)
Patients with B cell dysfunction, asplenia (as in sickle cell disease / after splenectomy) and complement defects are highly susceptible to infection with encapsulated organisms
Buprenorphine is a?
A. Partial mu agonist
B. Full mu agonist
C. Partial kappa agonist
D. Full kappa agonist
Correct answer : A. Partial mu agonist
Buprenorphine – Pharmacology
Buprenorphine is a semi-synthetic, mixed opioid agonist–antagonist
It is a partial mu agonist and a kappa antagonist
It is used as an analgesic and also for treatment of opioid addiction
Process used in an expression vector to increase yield of recombinant protein synthesis ?
A. Translation initiation
B. Promoter induction
C. Transcription terminators
D. Multiple cloning sites
Correct answer : B. Promoter induction
Expression vectors and recombinant protein synthesis
Expression vectors are plasmids / viruses designed to regulate protein expression in a target cell
They are used to insert a specific gene into the target cell to produce the desired protein
They contain regulatory sequences which act as enhancer and promoter regions to bring about efficient transcription of the gene
An inducible promoter regulates the gene expression and can increase the yield of the recombinant protein
Site of urea cycle is?
A. Liver
B. Kidney
C. GIT
D. Lungs
Correct answer : A. Liver
Site of urea cycle
Urea cycle (also known as ornithine cycle / Krebs Henseleit cycle) takes place in the liver
It is responsible for the conversion of toxic ammonia (produced by amino acid catabolism) to urea for excretion
5 enzymes are involved in the urea cycle are:
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
Ornithine transcarbamylase
Argininosuccinate synthase
Argininosuccinate lyase (also known as argininosuccinase)
Arginase
The first 2 enzymes are located in the mitochondria, whereas the other 3 are located in the cytoplasm
The rate limiting enzyme is Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
A patient presents to the emergency department with an abdominal trauma with signs of shock and peritonitis. Airway and breathing were checked. 2 large bore cannulas were inserted to secure IV access. What is the next step in the management of this patient?
A. Immediate exploratory laparotomy with general anaesthesia
B. Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma (FAST)
C. Laparoscopic visualisation of the injury
D. Watch and wait
Correct answer : A. Immediate exploratory laparotomy with general anaesthesia
Management of a case of abdominal trauma
Maintenance of airway, breathing and circulation is the first priority
The patient should be intubated in case of airway block
If the breathing is compromised, the patient should be ventilated with a high fraction of inspired oxygen
Large bore IV cannulas should be inserted and IV fluids should be administered
In case of external bleeding, direct pressure should be applied to control it
Spinal immobilisation should be done in cases with suspected spinal cord injury
Indications for laparotomy in blunt trauma abdomen
Hemodynamically unstable patients with shock
Signs of peritonitis
Progressive deterioration of the patient’s status
Identification of hemoperitoneum after Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma (FAST) or Diagnostic Peritoneal Lavage (DPL)
Non surgical management
If the patent is hemodynamically stable, further investigations like CT scan can be done to visualise the site of injury
Most common malignant orbital tumor in children is?
A. Acute myeloid leukemia
B. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
C. Rhabdomyosarcoma
D. Cavernous hemangioma
Correct answer : C. Rhabdomyosarcoma
Most common malignant orbital tumor in children is rhabdomyosarcoma.
Most common benign orbital tumor in children is dermoid cyst.
Sterile pyuria is characteristic of ?
A. Chronic hydronephrosis
B. Renal cell carcinoma
C. Renal tuberculosis
D. Nephroblastoma
Correct answer : C. Renal tuberculosis
Sterile pyuria
Sterile pyuria refers to the presence of more than 5 white blood cells (WBC’s) per high power field in the absence of bacteria in a routine urine specimen
It can be either due to various causes
Infectious etiology
Systemic conditions
Structural defects of kidney
Intrinsic renal pathology
Although hydronephrosis can also cause sterile pyuria, it is a characteristic feature of renal tuberculosis
Reabsorption of water in the GIT is maximum in?
A. Duodenum
B. Jejunum
C. Ileum
D. Colon
Correct answer : B. Jejunum
Daily turnover of water in the gastrointestinal system
Input of water in the GIT
Ingested water – 2000 ml
Endogenous secretions – 7000 ml
Salivary glands – 1500 ml
Stomach – 2500 ml
Bile – 500ml
Pancreas – 7000 ml
Total input – 9000 ml
Reabsorption of water in the GIT
Jejunum – 5500 ml
Ileum – 2000 ml
Colon – 1300 ml
Total reabsorption – 8800 ml
Water lost in stool – 200 ml
Ref: Ganong 22nd ed, p476
Not included among posterior relations of head of pancreas?
A. Terminal part of renal vein
B. Right crus of diaphragm
C. Common bile duct
D. First part of duodenum
Correct answer : D. First part of duodenum
First part of duodenum lies anterior to the head of pancreas.
Posterior relations of head of pancreas:
Aorta ( lies posterior to uncinate process )
Inferior venacava
Terminal part of right renal vein
Bile duct
Right crus of diaphragm
Most common cause of premature death in schizophrenia is?
A. Drug toxicity
B. Nosocomial infection
C. Homicide
D. Suicide
Correct answer : D. Suicide
Premature death in schizophrenia
Life expectancy of patients with schizophrenia is decreased by approximately 15 to 25 years. 1
Suicide is the most important cause of premature death in patients with schizophrenia.
There is a 20 fold increased risk of suicide compared to the general population.
Suicide attempts may occur without warning or expression of intent.
Cancer is the second most frequent cause of mortality in schizophrenics. 2
The rates of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disorders are also increased. 2
Journal references:
The paradox of premature mortality in schizophrenia: new research questions, J Psychopharmacol. 2010 November
Cancer mortality in patients with schizophrenia : A 11-year prospective cohort study, Cancer, Volume 115, Issue 15, pages 3555–3562, 1 August 2009
Which of the following contrast agents can be used in a patient with renal dysfunction for the prevention of contrast nephropathy?
A. Low osmolar contrast
B. Ionic contrast
C. Fenoldopam
D. Acetylcysteine
Correct answer : A. Low osmolar contrast
Prevention of contrast nephropathy
Non ionic low osmolar contrast agents are preferred in patients with decreased renal function to prevent contrast nephropathy
Ionic contrast media have a higher risk for contrast nephropathy, and hence should be avoided
The amount of contrast media used should be limited
The patient should be well hydrated before the procedure
Supplementary interventions include use of N-acetylcysteine, fenoldopam, theophylline, prostaglandins and magnesium
Contraindications to vasoconstrictors in local anaesthesia?
A. Spinal anaesthesia
B. Epidural anaesthesia
C. Digital nerve block
D. Regional anaesthesia
Correct answer : C. Digital nerve block
Contraindications to vasoconstrictors in local anaesthesia
Vasoconstrictors like adrenaline are used with local anaesthetics for decreasing the systemic absorption and to increase the local anaesthetic concentration and duration of nerve block
But adrenaline should not be used with lignocaine when infiltrating areas of end arterial supply
These sites include:
Fingers
Toes
Pinna
Penis
Nose
The use of adrenaline is these areas can compromise the blood flow and result in ischaemic injury
Blaschko’s lines represent?
A. Lines of development
B. Dermatomes
C. Lines along blood vessels
D. Lines along lymphatics
Correct answer : A. Lines of development
Blaschko’s lines
Blaschko’s lines are invisible developmental lines of the skin
They are thought to represent the pathways of epithelial migration and proliferation in the foetus
These were first demonstrated by German dermatologist Alfred Blaschko in 1901.
They do not correspond to the path of vessels / nerves / lymphatics
Many skin lesions follow Blaschko’s lines. eg: Incontinentia pigmenti, Linear lichen planus, Lichen striatus Naevus achromicus
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of Blount’s disease?
A. Genu valgum
B. Genu varum
C. Coxa vara
D. Coxa valga
Correct answer: B. Genu varum
Blount’s Disease
It is named after Walter Putnam Blount
It is also known as: Tibia vara, Mau-Nilsonne Syndrome, Blount-Barber syndrome, Erlacher-Blount syndrome, Osteochondrosis deformans tibiae
It is a growth disorder of the tibia resulting in progressive bow leg deformity
It is also associated with internal tibial torsion and genu recurvatum
It is mainly seen in children and adolescents
Treatment is by bracing and/or surgery
Endolymphatic hydrops is characteristic of:
A. Cholesteatoma
B. Meniere’s disease
C. Otosclerosis
D. Gradenigo’s syndrome
Correct answer: B. Meniere’s disease
Endolymphatic hydrops
It is another name for Meniere’s disease
In this condition, the endolymphatic sac in the inner ear is distended
This is either due to increased production of endolymph by the Stria vascularis or decreased absorption through the endolymphatic sac
More commonly seen in males
Clinical features – Vertigo, tinnitus, fluctuating hearing loss, aural fullness
Causes of primary amenorrhoea are all except
A. Turner syndrome
B. Sheehan’s syndrome
C. MRKH syndrome
D. Kallmann syndrome
Correct answer : B. Sheehan’s syndrome
Sheehan’s syndrome results in secondary amenorrhoea.
Causes of primary amenorrhoea
Turner syndrome (45 XO)
Swyer syndrome (46 XY, streak gonads, female phenotype)
Testicular feminisation syndrome (46 XY, insensitivity to androgen, female phenotype)
Mullerian agenesis ( Mayer Rokitansky Kuster Hauser [MRKH] syndrome)
Cryptomenorrhea – Imperforate hymen / vaginal septum
Kallmann syndrome (Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with hyposmia / anosmia)
Pituitary neoplasms
A primigravida in the first trimester of pregnancy was found to be sputum positive for acid fast bacilli. There is no prior history of tuberculosis. What is the treatment of choice for this patient?
A. Category I DOTS
B. Category II DOTS
C. Category III DOTS
D. Start ATT after delivery
Correct answer : A. Category I DOTS
Anti tuberculosis treatment in pregnancy
Newly smear positive cases of Tuberculosis are treated with Category I DOTS (Directly Observed Treatment Short course) in India.
The drugs given in category I DOTS – Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol and Pyrazinamide are not contraindicated in pregnancy
But if the disease is not treated properly, it is harmful for the foetus
Streptomycin is not given in pregnant patients as it is teratogenic
Right sided isomerism is found in association with?
A. Asplenia
B. Single spleen
C. Two spleens
D. Multiple spleens
Correct answer : A. Asplenia
Right sided isomerism
Alternate names – Ivemark syndrome / asplenia syndrome
It is a type of situs anomaly
Features : asplenia, malrotation of bowel, transverse liver, gall bladder agenesis, imperforate anus, horseshoe adrenal gland, urethral valves
The patients are immunocompromised due to absence of spleen, most die before 1 year of age
Which of the following is not a component of Total Parenteral Nutrition?
A. Amino acids
B. Fats
C. Vitamins
D. Fiber
Correct answer : D. Fiber
Components of total parenteral nutrition
Total parenteral nutrition should provide both energy and other essential nutrients.
Carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids provide energy.
The other essential nutrients to be included are: minerals, vitamins and water.
Dietary fiber is required only in case of enteral nutrition. It is not given as a part of parenteral nutrition.
Related reading: ESPEN (The European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism): Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Intensive care
Which of the following is responsible for drug induced pulmonary fibrosis?
A. Phenytoin
B. Bleomycin
C. Actinomycin D
D. Cisplatin
Correct answer : B. Bleomycin
Drug induced pulmonary fibrosis – Bleomycin
Bleomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic obtained from Streptomyces verticillus. It is used for the treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, squamous cell carcinomas, and testicular cancer. Bleomycin therapy can result in life-threatening interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. This side effect is seen about 10 percent of patients treated with Bleomycin. There is destruction of Type 1 pneumocytes with hyperplasia of type II pneumocytes.
Other drugs causing pulmonary fibrosis include : Methotrexate, Amiodarone, Busulfan, Sulfasalazine, Carmustine
Recent Research : Sorafenib found to ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis – Cell Death Dis. 2013 Jun 13;4:e665
Tetracycline is used for the prophylaxis of?
A. Brucellosis
B. Leptospirosis
C. Cholera
D. Meningitis
Correct answer : C. Cholera
Drug of choice for chemoprophylaxis of cholera is tetracycline. Doxycycline can also be used. Chemoprophylaxis is given for household contacts of cholera patients / in case of an outbreak in a closed community. But it is not given in case of mass outbreaks of cholera.
Rave drug is?
A. Cannabis
B. Hashish
C. Ecstasy
D. Heroin
Correct answer : C. Ecstasy
MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine), widely known as ‘Ecstasy‘ is a psychoactive drug with stimulant and hallucinogenic effects. It produces euphoria. It is consumed by individuals attending clubs and parties.
Which of the following is an integrase inhibitor currently in use for the treatment of HIV infection?
A. Indinavir
B. Elvitegravir
C. Saquinavir
D. Raltegravir
Correct answer : D. Raltegravir
Integrase inhibitors inhibit the enzyme ‘integrase‘ which inserts the viral genome into the host DNA.
Raltegravir was the first integrase inhibitor approved by the US FDA (in 2007).
Elvitegravir and Dolutegravir are 2 other integrase inhibitors approved in 2012 and 2013 respectively
Raltegravir is the correct answer because at the time of the exam (AIPG 2011), it was the only integrase inhibitor available commercially
Tolerance develops to all of the following effects of opioids except?
A. Euphoria
B. Miosis
C. Analgesia
D. Nausea
Correct answer : B. Miosis
Opioid tolerance does not develop for Constipation, Convulsions and Miosis.
Pulmonary compliance is not decreased in?
A. COPD
B. Decreased surfactant production
C. Pulmonary congestion
D. Pulmonary fibrosis
Correct answer : A. COPD
Pulmonary compliance is increased in emphysema (a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). In the other 3 conditions ( Decreased surfactant production, Pulmonary congestion and Pulmonary fibrosis), the pulmonary compliance is decreased.
Where is the urethral crest located?
A. Membranous urethra
B. Penile urethra
C. Prostatic urethra
D. Bulbar urethra
Correct answer : C. Prostatic urethra
The posterior wall of the prostatic urethra contains a longitudinal midline ridge known as the urethral crest.
Not an action of bradykinin?
A. Bronchodilation
B. Vasodilatation
C. Pain
D. Increase in vascular permeability
Correct answer : A. Bronchodilation
Bradykinin is a bronchoconstrictor.
Which of the following is used to decrease the toxicity of amphotericin B?
A. Dose reduction
B. Liposomal delivery systems
C. Supplementing glucose
D. Giving it along with flucytosine
Correct answer : B. Liposomal delivery systems
Liposomal delivery systems decrease the amount of free drug in the blood. Infected cells interact with the liposomes, resulting in the release of amphotericin B at the site of action.
An otherwise healthy male presented to the OPD with a curdy white patch on the tongue. The most probable diagnosis is?
A. Candidiasis
B. Lichen planus
C. Histoplasmosis
D. Aspergillosis
Correct answer : A. Candidiasis
White curdy patch in the oral cavity in an otherwise healthy individual is characteristic of candidiasis. But immunosuppressive conditions like HIV should be ruled out.
Most common laser used in laryngeal surgery is?
A. Argon laser
B. Nd YAG laser
C. CO2 laser
D. KTP laser
Correct answer : C. CO2 laser
CO2 does not penetrate into the deep tissue, hence there is decreased risk of scarring.
Triad of Klippel Feil syndrome consists of all except?
A. Low hair line
B. Elevated scapula
C. Short neck
D. Limited neck movements
Correct answer : B. Elevated scapula
Elevated scapula can be seen as a part of Klippel Feil syndrome. But it does not constitute the characteristic triad.
Drug of choice for treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy is ?
A. Ursodeoxycholic acid
B. Dexamethasone
C. Antihistamines
D. Cholestyramine
Correct answer : A. Ursodeoxycholic acid
Ursodeoxycholic acid decreases bile salt levels and relieves pruritus. It can also decrease the chance for fetal complications.
Which is not used for the treatment of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy?
A. Zonisamide
B. Topiramate
C. Carbamazepine
D. Valproate
Correct answer : C. Carbamazepine
Use of carbamazepine / phenytoin may increase myoclonus in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
Most common splenic cyst is?
A. Dermoid cyst
B. Hydatid cyst
C. Pseudocyst
D. Lymphangioma
Correct answer : B. Hydatid cyst
Hydatid cyst (caused by Echinococcus) is the most common type of splenic cyst.
Surgery for correction of cryptorchidism is best done before?
A. 1 month of age
B. 6 months of age
C. 1 year of age
D. 2 years of age
Correct answer : C. 1 year of age
Surgical orchidopexy should be done if spontaneous descent has not occurred by 1 year of age.
Use of streptokinase is contraindicated in?
A. Pulmonary embolism
B. AV fistula
C. Thrombophlebitis
D. Intracranial tumour
Correct answer : D. Intracranial tumour
Absolute contraindications for thrombolysis:
Previous history of intracranial haemorrhage
Cerebral vascular lesions (like AV malformations)
Intracranial malignancy
Suspected aortic dissection
Bleeding diathesis
Bence Jones proteins are derived from?
A. Alpha globulins
B. Beta globulins
C. Delta globulins
D. Gamma globulins
Correct answer: D. Gamma globulins
Bence Jones proteins contain light chains of gamma globulins.
Which is not a synthetic pyrethroid?
A. DDT
B. Proparthrin
C. Cypermethrin
D. Permethrin
Correct answer : A. DDT
DDT is an organochlorine compound. The other 3 are pyrethroids.
Which is not a feature of aconite poisoning?
A. Chest pain
B. Increased blood pressure
C. Tingling and numbness
D. Hypersalivation
Correct answer : B. Increased blood pressure
Hypotension is a a feature of aconite poisoning, not hypertension.
Which is not a feature of apoptosis?
A. Nuclear compaction
B. Cellular swelling
C. Cytoplasmic eosinophilia
D. Intact cell membrane
Correct answer : B. Cellular swelling
Cell skrinkage is seen in apoptosis.
False statement regarding phenytoin is?
A. It is a teratogenic drug
B. Highly protein bound
C. Induces insulin secretion
D. Follows saturation kinetics
Correct answer : C. Induces insulin secretion
Phenytoin inhibits insulin secretion and causes hyperglycemia.
MAO inhibitors are contraindicated in a patient taking?
A. Pethidine
B. Buprenorphine
C. Morphine
D. Pentazocine
Correct answer : A. Pethidine > D. Pentazocine
Use of MAO inhibitors in patient taking pethidine / pentazocine can precipitate serotonin syndrome.
Otoacoustic emissions arise from?
A. Inner hair cells
B. Outer hair cells
C. Organ or Corti
D. None of the above
Correct answer : B. Outer hair cells
Kayser Fleischer ring is characteristic of ?
A. Pterygium
B. Scleritis
C. Hemochromatosis
D. Wilson’s disease
Correct answer : D. Wilson’s disease
Wilson’s disease is characteristic of Wilson’s disease. Other conditions in which KF ring is seen are: Chronic active hepatitis, Primary biliary cirrhosis and Intrahepatic cholestatic syndromes.
Conditions associated with thymoma are all except?
A. Myasthenia gravis
B. Cushing’s syndrome
C. SIADH
D. Hypogammaglobulinemia
Correct answer : C. SIADH
SIADH ( Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH secretion) is not seen associated with thymomas.
Mass chemoprophylaxis in an endemic area is given for all except?
A. Leprosy
B. Yaws
C. Trachoma
D. Filariasis
Correct answer : A. Leprosy
Mass chemoprophylaxis is not given for preventing leprosy.
Marker for langerhans cell histiocytosis is?
A. CD 5
B. CD 1a
C. CD 22
D. CD 30
Correct answer : B. CD 1a
Immunohistochemical markers for langerhans cell histiocytosis are :
CD1a
HLADR
CD 68
S100
Langerin
Virus responsible for non immune hydrops foetalis is?
A. Cytomegalovirus
B. Herpes simplex virus
C. Hepatitis B virus
D. Parvovirus
Correct answer : D. Parvovirus
Parvovirus is the commonest infectious etiology for hydrops foetalis. The other viruses implicated include Cytomegalovirus, Hepatitis B virus, Herpes simplex virus, Rubella virus and Adenovirus.
Most common cause of meningoencephalitis in children is?
A. HSV
B. Measles
C. Arbobvirus
D. Enterovirus
Correct answer : D. Enterovirus
Enteroviruses are the most common cause of viral meningoencephalitis in children.
Commonest site of urethral carcinoma in males is?
A. Prostatic urethra
B. Penile urethra
C. Bulbomembranous urethra
D. Navicular fossa
Correct answer : C. Bulbomembranous urethra
Commonest site of urethral carcinoma in males is Bulbomembranous urethra. It constitutes about 60% of the cases. Penile urethra is involved in 30% and prostatic urethra is involved in 10%.
Bence Jones proteinuria is seen in?
A. Alpha heavy chain disease
B. Gamma heavy chain disease
C. Mu heavy chain disease
D. Epsilon heavy chain disease
Correct answer : C. Mu heavy chain disease
Bence Jones proteinuria is seen in Mu heavy chain disease. It occurs due to the excretion of kappa light chains in urine.
JSY is an acronym for?
A. Janani Suraksha Yojana
B. Jeevan Suraksha Yojana
C. Jeevan Shakthi Yojana
D. Jan Suraksha Yojana
Correct answer : A. Janani Suraksha Yojana
Janani Suraksha Yojana is a centrally funded scheme launched in 2005 offering maternity benefits. It aims at lowering maternal mortality and infant mortality by encouraging institutional deliveries.
Which of the following is used for narcoanalysis?
A. Atropine
B. Phenobarbitone
C. Pethidine
D. Scopolamine
Correct answer : D. Scopolamine
Drugs used for narcoanalysis are:
Scopolamine (hyoscine)
Sodium thiopental (Sodium Pentothal)
Amobarbital (Amytal Sodium)
Secobarbital sodium (Seconal)
Latent varicella zoster infection is found in?
A. T cells
B. B cells
C. Macrophages
D. Trigeminal ganglion
Correct answer : D. Trigeminal ganglion
Latent varicella zoster virus is found in sensory ganglia.
A person who is heterozygous for sickle cell anemia has increased resistance for?
A. Malaria
B. Filariasis
C. Dengue haemorrhagic fever
D. Thalassemia
Correct answer : A. Malaria
Sickle cell trait (heterozygous case of sickle cell anemia) provides protection against malaria. Sickling of RBC’s result in the leaking of potassium from the cell. This leads to the death of the malarial parasites within the RBC’s.
Ethosuximide is the drug of choice for treatment of ?
A. Generalized tonic clonic seizures
B. Absence seizures
C. Simple partial seizures
D. Complex partial seizures
Correct answer : B. Absence seizures
Ethosuximide is the drug of choice for treatment of absence seizures. Other drugs used in the management of absence seizures are valproic acid, lamotrigine and clonazepam.
Rothera’s test is utilised for detection of?
A. Glucose
B. Proteins
C. Urea
D. Ketone bodies
Correct answer : D. Ketones
Tests in biochemistry:
Ketone bodies – Rothera’s test
Reducing sugars – Benedict’s test, Fehling’s test
Proteins – Heller’s nitric acid test, Heat and acetic acid test
Bile salts – Hay’s test
Bile pigments – Fouchet’s test
Blood – Benzidine test
Sphingomyelinase deficiency is characteristic of ?
A. Fabry disease
B. Krabbe’s disease
C. Tay Sachs disease
D. Niemann Pick disease
Correct answer : D. Niemann Pick disease
Sphingomyelinase deficiency is seen in Niemann Pick disease. The enzymes deficient in the other disease are:
Fabry disease – alpha galactosidase
Krabbe’s disease – beta galactosidase
Tay Sachs disease – Hexosaminidase A
Which of the following is seen in Burkitt’s lymphoma?
A. t(8:14)
B. t(15:17)
C. t(X:18)
D. t(11:14)
Correct answer : A. t(8:14)
t(8:14) is the most common (70% of cases) translocation seen in Burkitt’s lymphoma.
Which is not a cognitive dysfunction?
A. Overgeneralization
B. Thought block
C. Catastrophic thinking
D. Arbitrary inference
Correct answer : B. Thought block
Cognitive dysfunction refers to the errors in the processing of information in the thought process. Thought block is an error in the continuity of thought.
Egg on side appearance is characteristic of?
A. Tetralogy of fallot
B. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
C. Patent ductus arteriosus
D. Transposition of great arteries
Correct answer : D. Transposition of great arteries
‘Egg on side’ or ‘Egg on string’ appearance is characteristic of transposition of great arteries.
Brown tumour is characteristic of?
A. Hyperparathyroidism
B. Hypoparathyroidism
C. Hyperthyroidism
D. Hypopituitarism
Correct answer : A. Hyperparathyroidism
Brown tumour occurs due to the increased osteoclastic activity in hyperparathyroidism. It is a benign mass of reactive tissue.
Arden index is used for interpretation of?
A. Visual evoked response
B. Electrooculogram
C. Electroretinogram
D. Visual field charting
Correct answer : B. Electrooculogram
Arden index is used for interpretation of an electrooculogram.
Increased nuchal translucency in 13th week fetal ultrasound characteristic of ?
A. Turner syndrome
B. Down’s syndrome
C. Hydrocephalus
D. Klinefelter syndrome
Correct answer : B. Down’s syndrome
Down’s syndrome is the most common cause of increased nuchal translucency in fetal ultrasound. The other causes are Trisomy 13, Trisomy 18, Klinefelter syndrome & Turner’s syndrome.
The commonest cause of abdominal aortic aneurysm is?
A. Trauma
B. Syphilis
C. Vasculitis
D. Atherosclerosis
Correct answer : D. Atherosclerosis
90% of all abdominal aortic aneurysms greater than 4 cm are caused by atherosclerotic disease.
First autologous renal transplantation was performed by?
A. Hardy
B. Higgins
C. Studor
D. Kavosis
Correct answer : A. Hardy
First autologous renal transplantation was done by Hardy in the year 1963.
Which of the following is impaired in a case of gout?
A. Protein metabolism
B. Ketone metabolism
C. Purine metabolism
D. Pyrimidine metabolism
Correct answer : C. Purine metabolism
Gout arises form the increased production / decreased excretion of uric acid (an end product of purine metabolism).
A case of Acute Flaccid Paralysis should be kept under surveillance for residual paralysis for?
A. 30 days
B. 45 days
C. 60 days
D. 90 days
Correct answer : C. 60 days
Caspases are involved in ?
A. Apoptosis
B. Necrosis
C. Neoplasia
D. Inflammation
Correct answer : A. Apoptosis
Caspases are cysteine proteases which play an important role in apoptosis.
Which of the following drugs have a narrow therapeutic index?
A. Lithium
B. Diazepam
C. Penicillin
D. Desipramine
Correct answer : A. Lithium
Other drugs with narrow therapeutic index:
Digoxin
Gentamicin
Amphotericin B
Levothyroxine
Prazosin
Theophylline
Quinidine
Warfarin
Valproic acid
Lymphatic drainage from the spongy urethra is towards?
A. Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
B. Deep inguinal lymph nodes
C. External iliac lymph nodes
D. Internal iliac lymph nodes
Correct answer : B. Deep inguinal lymph nodes
Lymphatic drainage of urethra
Prostatic and membranous urethra – Mainly to internal iliac lymph nodes, partly to external iliac lymph nodes
Spongy urethra – Mainly to deep inguinal lymph nodes, partly to superficial inguinal and external iliac lymph nodes
Which of the following are vitamin K dependant clotting factors?
A. II and IV
B. IX and X
C. III and V
D. VI and VII
Correct answer : B. IX and X
Vitamin K dependant clotting factors are II, VII, IX and X. Vitamin K is required for the gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid residues.
Most ionizing radiation among the following is?
A. X rays
B. Gamma rays
C. Alpha rays
D. Beta rays
Correct answer : C. Alpha rays
Alpha rays have the highest ionization power, whereas gamma rays have the highest penetration power.
Which of the following is tested using the ‘Lift off test’ ?
A. Teres Minor
B. Subscapularis
C. Supraspinatus
D. Infraspinatus
Correct answer : B. Subscapularis
Lift off test, also know as Gerber’s test is used to assess the function of the subscapularis muscle. For performing this test, the arm is extended and internally rotated so that the dorsum of hand rests on the lower back. The patient is asked to lift the hand off the back. This requires internal rotation of the arm brought about by the subscapularis. If the patient is able to perform the maneuver, the subscapularis function is normal and the test is negative.
All of the following are involved in endophthalmitis except?
A. Retina
B. Vitreous
C. Sclera
D. Uvea
Correct answer : C. Sclera
Endophthalmitis does not involve the scleral coat of the eye. Sclera in involved only in panophthalmitis.
Which of the following is used for the treatment of chlamydia infection in pregnancy?
A. Tetracycline
B. Erythromycin
C. Azithromycin
D. Doxycycline
Correct answer : C. Azithromycin
Preferred agent for treatment of chlamydia infection in pregnancy in azithromycin. It is given as a single dose of 1g leading to high compliance rate.
Which among the following is most commonly associated with carcinoma cervix?
A. HPV 35
B. HPV 33
C. HPV 18
D. HPV 16
Correct answer : D. HPV 16
HPV 16 is most commonly associated with carcinoma cervix. It is responsible for 40-70% of all invasive squamous cell cervical cancers.
Which of the following maneuvers is not used for the management of shoulder dystocia?
A. McRoberts maneuver
B. Suprapubic pressure
C. Woods corkscrew maneuver
D. Mauriceau Smellie Veit maneuver
Correct answer : D. Mauriceau Smellie Veit maneuver
Mauriceau Smellie Veit maneuver is used in the management of after coming head in case of breech delivery.
What is shoulder dystocia?
It is a type of obstructed labour in which the anterior shoulder of the fetus fails to deliver after the emergence of the head.
Risk factors
Diabetes
Fetal macrosomia
Procedures used in the management of shoulder dystocia
McRoberts maneuver – The mothers thighs are abducted and flexed onto her abdomen.
Rubin I maneuver (suprapubic pressure)
Rubin II maneuver (posterior pressure on anterior shoulder)
Wood’s corkscrew maneuver – This is performed only if suprapubic pressure and McRoberts maneuver are unsuccessful. Here, the posterior shoulder is rotated to anterior position.
Jacquemier’s maneuver (Barnum’s maneuver) – Delivery of the posterior shoulder first
Gaskin maneuver – Mother is moved to an all fours position with the back arched. This widens the pelivic outlet
Zavanelli’s maneuver
Cleidotomy – one or both clavicles are cut to decrease the diameter of the shoulder girdle. This is done only in case of a dead fetus / anencephalic fetus
Maternal symphysiotomy – the pubic symphysis of the mother is cut to facilitate the delivery of the shoulder (this is rarely used)
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are useful in the management of ?
A. Acute myeloid leukemia
B. Small cell carcinoma of lung
C. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors
D. Neurofibromatosis
Correct answer : C. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are used in the treatment of:
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia ( philadelphia chromosome positive cases )
Head and neck malignancies
Non small cell carcinoma lung
Gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Hepatocellular cancer
Renal cell carcinoma
Pancreatic cancer
Colorectal cancer
Which of the following is seen associated with alcoholic paranoia ?
A. Drowsiness
B. Delusions
C. Hallucinations
D. Impulsiveness
Correct answer : B. Delusions
Alcoholic paranoia is an alcohol induced psychotic disorder
It is characterised by delusions (mostly of persecution / jealousy / reference)
Auditory hallucinations may also be seen
Which anaesthetic agent is preferred in a patient taken for surgery with bilirubin of 8.6 mg/dl and serum creatinine of 2.1 mg/dl ?
A. Atracurium
B. Vecuronium
C. Pancuronium
D. Rocuronium
Correct answer : A. Atracurium
Atracurium is the preferred muscle relaxant in a patient with liver dysfunction / renal failure
It undergoes non specific ester hydrolysis and non enzymatic degradation ( Hoffman degradation )
It does not depend on the liver / kidney for its deactivation
Other muscle relaxants that can be given in liver / renal disease are Cisatracurium and Mivacurium
Which of the following substances are used to coat the walls of a CT scan room for radiation shielding?
A. Tungsten
B. Glass
C. Lead
D. Iron
Correct answer : C. Lead
Lead is used as radiation shielding in CT scans, X-ray machines etc.
All are features of autistic disorders except ?
A. Stereotypic movements
B. Impairment of social interaction
C. Visual impairment
D. Delay in speech development
Correct answer : C. Visual impairment
Autistic disorders are characterised by:
Impairement of social interaction
Disorder of communication and language (as in delayed development of speech)
Stereotypic movements
Visual impairment is not seen in autism.
Structure not seen in bronchoscopy?
A. Vocal cords
B. Trachea
C. First segmental division of bronchi
D. Subcarinal lymph nodes
Correct answer : D. Subcarinal lymph nodes
Structures seen in bronchoscopy are : Uvula, Epiglottis, Vocal cords, Larynx, Trachea, Carina, Segmental bronchi, Subsegmental bronchi
Subcarinal lymph nodes cannot be seen as they are located outside the trachea
Lord’s plication is used in the treatment of ?
A. Hydrocele
B. Inguinal hernia
C. Testicular malignancy
D. Varicocele
Correct answer : A. Hydrocele
Lord’s plication is a surgical procedure used for the treatment of hydrocele
The hydrocele fluid is drained and the redundant sac is plicated
It is used for treatment of small and medium sized hydroceles
Which of the following structures are connected by Grayhack shunt?
A. Corpora cavernosa and saphenous vein
B. Corpora cavernosa and dorsal vein
C. Corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum
D. Corpora cavernosa and glans
Correct answer : A. Corpora cavernosa and saphenous vein
Grayhack shunt connects the corpora cavernosa with the saphenous vein
It is used for the treatment of ischaemic priapism
Which of the following parasites can cause biliary obstruction?
A. Clonorchis sinensis
B. Enterobius ( Pin worm)
C. Strongyloides stercoralis
D. Ancylostoma duodenale
Correct answer : A. Clonorchis sinensis
Parasites which can cause biliary obstruction:
Cestodes – Echinococcus granulosus
Trematodes – Fasciola hepatica, Opisthorchis, Clonorchis sinensis
Nematodes – Ascaris lumbricoides
Movement across socioeconomic levels is known as?
A. Social insurance
B. Social mobility
C. Social equality
D. Social upliftment
Correct answer : B. Social mobility
The socioeconomic status of an individual / family can change over time due to the change in their literacy, job and income
An individual belonging to a low socioeconomic class can move to a higher class by means of better income
Similarly, an individual in a higher class may move to a lower class due to loss of his job
This change in socioeconomic status of an individual / family over time is known as Social Mobility
Most common cause of Down’s syndrome is?
A. Translocation
B. Mosaicism
C. Paternal nondisjunction
D. Maternal nondisjunction
Correct answer : D. Maternal nondisjunction
Maternal nondisjunction in meiosis I is the most common cause of Down’s syndrome (95% of total cases)
Which of the following is used in the treatment of meningococcal meningitis in patients allergic to penicillin?
A. Ciprofloxacin
B. Teicoplanin
C. Meropenem
D. Chloramphenicol
Correct answer : D. Chloramphenicol
Treatment of meningococcal meningitis:
Drug of choice – Penicillin G
In case of penicillin resistance, third generation cephalosporins should be used ( Ceftriaxone / Cefotaxime )
In case of penicillin / cephalosporin allergy, Chloramphenicol is used
All are true regarding synovial sarcoma except?
A. More common at extra articular sites
B. Knee and foot are commonly involved
C. Usually seen in individuals less than 50 years of age
D. Originates from the synovial lining
Correct answer: D. Originates from the synovial lining
The name synovial sarcoma is a misnomer
It does not arise from the synovial lining
The name arises from the fact that it histologically resembles synovial tissue
Most commonly seen in those between 15 and 35 years of age
Males and females are equally affected
Most commonly seen in the lower limbs, around knee and foot
It is a slow growing tumour with an indolent course (It may be aggressive in later stages)
Primary impact injury in case of road traffic accident are seen commonly in?
A. Face
B. Chest
C. Abdomen
D. Legs
Correct answer : D. Legs
Primary impact injuries are caused by the first impact of the vehicle with the pedestrian in an accident
The legs get hit most often (by the bumper in front of the vehicle)
The other injuries associated with a road traffic accident are the secondary impact injuries and secondary injuries
Secondary impact injury is caused by the second impact with the vehicle (eg: the body of thrown onto the vehicle / the vehicle runs over the body)
Secondary injuries are caused when the body strikes the ground after the collision
Which stain is used to study fungal morphology in tissue sections?
A. Periodic acid–Schiff
B. Alizarin Red
C. Masson’s Trichrome
D. Von Kossa
Correct answer : A. Periodic acid–Schiff
Stains used to demonstrate fungi are Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) and Methenamine Silver Stain
PAS stains both living and dead fungi, whereas Methenamine Silver stains only living fungi
Massons’s Trichrome is used to demonstrate collage, muscle and fibrin
Alizarin Red and Von Kossa are used to demonstrate calcium in tissues
Which is the type of joint seen in the growth plate?
A. Primary cartilaginous
B. Secondary cartilaginous
C. Fibrous joint
D. Plane Joint
Correct answer : A. Primary cartilaginous
Growth plate is a primary cartilaginous joint
They are also known as synchondrosis / hyaline cartilage joints
The bones are joined by a plate of hyaline cartilage
It does not permit any movement
Other examples: Costochondral joint, I chondro sternal joint, Spheno-occipital joint
Which of the following gives rise to the muscular component of dorsal aorta?
A. Intermediate mesoderm
B. Lateral plate mesoderm
C. Axial mesoderm
D. Paraxial mesoderm
Correct answer : B. Lateral plate mesoderm
Vascular smooth muscle cells are thought to arise from splanchnic layer of paraxial mesoderm. But recent studies have shown that the aortic smooth muscle cells arise from the lateral plate mesoderm.
Which of the following is false regarding delirium tremens?
A. Tremors
B. Ophthalmoplegia
C. Visual hallucinations
D. Clouding of consciousness
Correct answer : B. Ophthalmoplegia
Ophthalmoplegia is seen in Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
An eight year old boy presented to the casualty with high fever, pruritic erythematous rash, joint pain and lymph node enlargement. There is a history of upper respiratory tract infection for which he was on cefaclor – 8 days completed of a 10 day course. The most likely diagnosis is?
A. Serum sickness like illness
B. HSP
C. Type III hypersensitivity
D. Kawasaki disease
Correct answer : A. Serum sickness like illness
Serum sickness like reaction can occur following the use of certain drugs, especially cefaclor in children. It presents with an urticarial / purpuric rash, arthritis, lymphadenopathy and fever. But unlike true serum sickness (a type III hypersensitivity response), it is not caused by circulating immune complexes.
Gold standard test for laryngopharyngeal reflux is?
A. Esophageal motility study
B. Barium swallow
C. 24 hour double probe pH monitoring
D. Esophageal biopsy
Correct answer : C. 24 hour double probe pH monitoring
Gold standard test for laryngopharyngeal reflux is 24 hour double probe (lower esophagus and pharynx) pH monitoring.
Organism most commonly implicated in Late onset endophthalmitis after cataract surgery is?
A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
B. Staphylococcus epidermidis
C. Candida albicans
D. Propionibacterium acnes
Correct answer : D. Propionibacterium acnes
Propionibacterium acnes is a gram positive, non spore forming bacillus which is most commonly implicated in Late onset endophthalmitis after cataract surgery.
Decreased motility of Fallopian tube is seen associated with?
A. Noonan syndrome
B. PCOD
C. Churg Strauss syndrome
D. Kartagener’s syndrome
Correct answer: D. Kartagener’s syndrome
Ciliary motility is impaired in Kartagener’s syndrome.
A one year old child presented to the OPD with the history of short stature, tiredness and constipation. Examination revealed a palpable goitre. Serum T4 was decreased and TSH levels were increased. Which is the most probable diagnosis?
A. Thyroid dysgenesis
B. Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis
C. TSH receptor blocking antibody
D. Central hypothyroidism
Correct answer : B. Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis
Among the options given, only Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis presents with a palpable goitre.
Most common tumour associated with Neurofibromatosis I in children is?
A. AML
B. CML
C. ALL
D. JMML (Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia)
Correct answer : D. JMML (Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia)
Children with NF1 have a 200-500 times increased incidence of JMML.
Psammoma body is not seen in ?
A. Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
B. Follicular carcinoma of thyroid
C. Serous cystadenocarcinoma of ovary
D. Meningioma
Correct answer : B. Follicular carcinoma of thyroid
Psammoma bodies are seen in Papillary carcinoma of thyroid, Meningioma, Renal cell carcinoma and in Serous cystadenocarcinoma of ovary.
Coarctation of aorta is most commonly seen with?
A. ASD
B. VSD
C. PDA
D. Bicuspid aortic valve
Correct answer : D. Bicuspid aortic valve
Bicuspid aortic valve is the most common anomaly associated with coarctation of aorta (seen in 70%).
Contraindication for medical management of gallstone is:
A. Normal gallbladder function
B. Small gallstones
C. Radiolucent gallstones
D. Radiopaque gallstones
Correct answer : D. Radiopaque gallstones
Medical management cannot be used in case of radiopaque gallstones.
Which of the following conditions is associated with multiple cutaneous sebaceous adenomas?
A. Turcot’s syndrome
B. Cowden syndrome
C. Gardner’s syndrome
D. Muir Torre syndrome
Correct answer : D. Muir Torre syndrome
Multiple cutaneous sebaceous adenomas are seen in Muir Torre syndrome.
Which of the following renal calculi is seen associated with proteus infection?
A. Calcium Oxalate
B. Triple Phosphate
C. Xanthine
D. Uric Acid
Correct answer : B. Triple Phosphate
High ammonia concentration leads to the formation of triple phosphate stones. This arises when urine is infected with urea splitting organisms like Proteus.
All are true regarding Campylobacter jejuni except?
A. It is the commonest cause of campylobacteriosis
B. Humans act as important reservoirs
C. It is associated with Guillian Barre syndrome
D. Poultry is a common source of infection
Correct answer :B. Humans act as important reservoirs
Humans do not act as reservoirs for Campylobacter jejuni
Important reservoirs are poultry, cattle, swine and household pets
All of the following statements regarding Corynebacterium diphtheriae are true, except?
A. It can be identified by using tests for toxigenicity
B. The toxin inhibits protein synthesis
C. Toxin has adverse effects on cardiovascular and nervous systems
D. Native chromosome is responsible for toxin production
Correct answer : D. Native chromosome is responsible for toxin production
Toxin production is mediated by toxigenic bacteriophages. The gene is transmitted via transduction.
False regarding Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aures (MRSA) ?
A. Resistance may be produced by increased production of beta lactamase enzyme
B. Resistance is primarily plasmid mediated
C. Resistance is due to altered Penicillin Binding Proteins
D. Resistance may be missed at incubation temperature of 37°C during susceptibility testing
Correct answer : B. Resistance is primarily plasmid mediated
Resistance is mediated by the MeC-A gene which codes for altered Penicillin Binding Proteins. MeC-A gene is part of nuclear chromosomes.
False regarding Pneumococcus is?
A. Causes mild form of meningitis
B. Respiratory tract of carriers is the most important source of infection
C. Commonest cause of otitis media
D. Capsule is important in virulence
Correct answer : A. Causes mild form of meningitis
Pneumococcal meningitis is very severe and is fatal if untreated.
A patient presented to the OPD with clinical features of pneumonia. Sputum examination of the patient revealed a gram positive cocci with alpha hemolysis on sheep agar. Which test will you do to confirm the diagnosis?
A. Coagulase test
B. Bacitracin sensitivity
C. CAMP test
D. Bile solubility
Correct answer : D. Bile solubility
The clinical features and microbiological characteristics are suggestive of pneumococcal pneumonia
The diagnosis can be confirmed by Bile solubility and Optochin sensitivity
Which chemical is the most commonly used as a fixative for pathological specimens?
A. Picric acid
B. Mercuric chloride
C. Ethanol
D. Formaldehyde
Correct answer : D. Formaldehyde
Fixation is the process by which the morphological features of tissues are preserved
All of the above chemicals can be used a fixatives for pathological specimens
But formalin (solution of formaldehyde in water) is the most commonly used fixative
Formaldehyde is a colourless gas at room temperature with a pungent smell
Psammoma bodies are not seen in?
A. Meningioma
B. Papillary carcinoma thyroid
C. Follicular carcinoma thyroid
D. Serous cystadenocarcinoma of ovary
Correct answer: C. Follicular carcinoma thyroid
Psammoma bodies are characteristically seen in:
Papillary carcinoma thyroid
Meningioma
Serous cystadenocarcinoma of ovary
Renal cell carcinoma
Breast cancer, lung cancer, malignant mesotheliomas (occasional)
Which among the following is not a neuronal tumour?
A. Ependymoma
B. Ganglioglioma
C. Neurocytoma
D. Gangliocytoma
Correct answer : A. Ependymoma
Ependymoma is a glial tumour
It is derived from ependymal cells of the ventricles
Necrotizing lymphadenitis is a characteristic feature of?
A. Hodgkin’s disease
B. Kikuchi disease
C. Kimura disease
D. Castleman disease
Correct answer : B. Kikuchi disease
Lymphadenitis can be seen in all of the above mentioned diseases, but necrotizing lymphadenitis is seen only in Kikuchi disease.
Which among the following is not an autoimmune disease?
A. Myasthenia gravis
B. Systemic lupus erythematosus
C. Grave’s disease
D. Sickle cell disease
Correct answer : D. Sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease is a genetic condition which is characterised by mutation in beta globin chain of hemoglobin (glutamic acid is replaced with valine in the 6th position of beta chain)
Most commonly seen antibody in antiphospholipid antibody syndrome?
A. Anti beta 2 glycoprotein antibody
B. Anti nuclear antibody
C. Anti centromere antibody
D. Beta 2 microglobulin antibody
Correct answer : A. Anti beta 2 glycoprotein antibody
Other important antibodies seen in APLA syndrome are anti cardiolipin antibody and lupus anticoagulant.
False regarding Bernard Soulier Syndrome?
A. Large platelets
B. Decreased platelet count
C. Ristocetin aggregation normal
D. Platelet aggregation in response to collagen and ADP is normal
Correct answer : C. Ristocetin aggregation normal
In Bernard Soulier Syndrome, platelet response to ADP, collagen and Thrombin are normal.
But no aggregation occurs in response to Ristocetin.
It occurs due to defect in glycoprotein Ib – the receptor for von Willebrand factor
True statement regarding platelet function defects?
A. Normal platelet count with increased bleeding time
B. Decreased platelet count with increased bleeding time
C. Increased platelet count with increased bleeding time
D. Normal platelet count with normal bleeding time
Correct answer : A. Normal platelet count with increased bleeding time
In platelet function defects, there is normal platelet count with increased bleeding time
The defect lies in platelet function, not number
HbH is seen in which of the following conditions?
A. Deletion of 3 beta genes
B. Deletion of 3 alpha genes
C. Deletion of 4 beta genes
D. Deletion of 4 alpha genes
Correct answer : B. Deletion of 3 alpha genes
HbH is formed by 4 beta chains (tetramer of beta chains)
It is seen in alpha thalassemia with deletion of 3 alpha chains
It is precipitated as Heinz bodies within RBC’s
Deletion of 4 alpha chains results in formation of Hb Barts (gamma chain tetramer) and is incompatible with life
All are true about coagulation pathway except?
A. Intrinsic pathway can be activated in vitro
B. Calcium is necessary for several steps of coagulation pathway
C. Factor X is important in both extrinsic and intrinsic pathway
D. Extrinsic pathway activation is via contact negatively charged surfaces
Correct answer : D. Extrinsic pathway activation is via contact negatively charged surfaces
Extrinsic pathway is activated by exposure to tissue factor
Intrinsic pathway is activated by contact with negatively charged surfaces
All are true about Xanthogranulomatous inflammation except?
A. Associated with tuberculosis
B. Foam cells are present
C. Yellow nodules are present
D. Multi-nucleated giant cells are present
Correct answer : A. Associated with tuberculosis
Xanthogranulomatous inflammation is a condition in which lipid laden macrophages (foam cells) are deposited in various parts of the body
The exact etiopathogenesis is not known
E.coli and proteus are implicated as etiological agents
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is not considered as an etiological agent
Which of the following is most characteristic feature of acute inflammation?
A. Vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability
B. Margination of leukocytes
C. Vasoconstriction
D. Vascular stasis
Correct answer : A. Vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability
Vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability is the most characteristic feature of acute inflammation. Margination of leukocytes and vascular stasis are other prominent features.
Which of the following enzymes are responsible for generating ‘oxygen burst’ within neutrophils for killing intracellular bacteria?
A. Superoxide dismutase
B. Glutathione peroxidase
C. Oxidase
D. Catalase
Correct answer : C. Oxidase
NADPH oxidase is responsible for the ‘oxygen burst’ within neutrophils for killing intracellular bacteria
During the ‘oxygen burst’, there is an abrupt increase in oxygen consumption and increased synthesis of free radicals
All of the following enzymes may contribute in generating free oxygen radicals within neutrophils for killing intracellular bacteria except?
A. Superoxide dismutase
B. Fenton’s reaction
C. NADPH oxidase
D. Glutathione peroxidase
Correct answer : D. Glutathione peroxidase
Glutathione peroxidase is a free radical scavenger which converts H2O2 to H2O and O2. It does not generate free radicals.
Superoxide dismutase converts superoxide (O2–) to H2O2. Hence it is involved in both free radical scavenging and creation.
Which of the following organelles plays a pivotal role in Apoptosis?
A. Mitochondria
B. Endoplasmic Reticulum
C. Nucleus
D. Golgi Apparatus
Correct answer : A. Mitochondria
Apoptosis can be initiated by both intracellular and extracellular signals
Mitochondria plays an important role in mediating apoptosis initiated by intracellular signals
Cell surface death receptors play an important role in mediating apoptosis initiated by extracellular signals
Mineralocorticoid Receptors are found in all of the following, Except?
A. Liver
B. Colon
C. Hippocampus
D. Kidney
Correct answer : A. Liver
Alkalinization of urine is done during administration of which of the following chemotherapeutic drugs?
A. Ara-C (Cytarabine)
B. Methotrexate
C. Cisplatin
D. Ifosfamide
Correct answer : B. Methotrexate
Alkalinization of urine is used in patients receiving high dose methotrexate to promote renal excretion and to avoid nephrotoxicity
IV Sodium bicarbonate is used to maintain urine pH above 7.0 to avoid precipitation of methotrexate (a weak acid) in the acid pH of renal tubules
All of the following are known adverse effects of thalidomide, except:
A. Diarrhoea
B. Teratogenicity
C. Deep Vein Thrombosis
D. Peripheral Neuropathy
Correct answer : A. Diarrhoea
Constipation is a side effect with thalidomide intake, not diarrhoea.
Other adverse effects of thalidomide:
Peripheral neuropathy
Thromboembolism
Drowsiness
Teratogenicity
Fatigue
Which of the following antihypertensive drugs should not be used in a patient on Lithium in order to prevent Lithium Toxicity?
A. Clonidine
B. Beta blockers
C. Calcium Channel Blockers
D. Diuretics
Correct answer : D. Diuretics
Diuretics increase sodium loss in urine and increase lithium retention. Hence they should not be used in patients on Lithium.
Which of the following agents is used for the treatment of Thrombocytopenia secondary to myelosuppressive cancer chemotherapy?
A. Filgrastim
B. Sargramostim
C. Oprelvekin
D. Erythropoietin
Correct answer : C. Oprelvekin
Oprelvekin (Interleukin 11) is the only agent approved by the FDA for treatment of thrombocytopenia secondary to myelosuppressive cancer chemotherapy
Filgrastim (G-CSF) and Sargramostim (GM-SCF) are used in the treatment of neutropenia
Erythropoietin is used in treatment of anemia
All of the following statements about Aprepitant are true except?
A. Agonist at Neurokinin receptor (NK1)
B. Crosses blood brain barrier
C. Metabolised by CYP3A4 pathway
D. Ameliorates nausea and vomiting of chemotherapy
Correct answer : A. Agonist at Neurokinin receptor (NK1)
Aprepitant is an NK1 antagonist
It crosses blood brain barrier and blocks NK1 receptors
It has an anti emetic action and is used along with chemotherapy regimens
It is metabolised in liver via CYP3A4 pathway
It decreases metabolism of drugs metabolised by CYP3A4 pathway (can prolong prothrombin time in patients on warfarin)
All of the following statement s about ‘Erlotinib’ are true except?
A. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
B. Food decreases its absorption
C. Rashes may occur
D. Used in non small cell lung carcinoma
Correct answer : B. Food decreases its absorption
Oral bioavailability of erlotinib is 60%
But when taken along with food, it increases to 100%
It should be taken on an empty stomach as there is increased chance of side effects when taken along with food
It is used in treatment of non small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer
Important adverse effects are diarrhoea, acneform rash, fatigue and anorexia
All of the following statements about Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulator (SERD), Fulvestrant are true, Except
A. It is a selective estrogen antagonist
B. Used in the treatment of breast cancer
C. Slower acting, safer and less effective than SERM
D. May be administered as ‘once a month’ dose
Correct answer : C. Slower acting, safer and less effective than SERM
Fulvestrant is safer, faster acting and has a long duration of action compared to SERM’s.
All of the following statements about Ranolazine are true, except:
A. Piperazine derived antianginal agent
B. May be used as first line agent in chronic angina
C. May improve Glycemic control
D. Hypotension is an established adverse effect
Correct answer : D. Hypotension is an established adverse effect
Unlike other anti anginal agents, Ranolazine does not decrease heart rate / blood pressure.
It does not cause vasodilatation.
All of the following statements about meglitinides are true, except:
A. Act by stimulating insulin release
B. Decrease Postprandial Hyperglycemia
C. Hypoglycemia is less common than with sulfonylureas
D. Act by decreasing insulin resistance
Correct answer : D. Act by decreasing insulin resistance
Meglitinides act by increasing insulin release. They do not decrease insulin resistance.
lntegrase inhibitors approved for HIV is:
A. Raltegravir
B. lndinavir
C. Lopinavir
D. Elvitegravir
Correct answer : A. Raltegravir
Raltegravir received approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in October 2007.
Indinavir and Lopinavir are protease inhibitors.
Elvitegravir was approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 27, 2012. (But this question was asked in AIPG 2011)
Amphotericin B treatment mandates the monitoring of which of the following electrolytes:
A. Na+
B. Ca2+
C. K+
D. Mg2+
Correct answer : C. K+
Both potassium and magnesium are lost in urine during treatment with amphotericin B. Hence both electrolytes should be monitored. But monitoring potassium levels are more important as hypokalemia can cause cardiotoxicity.
Prolonged treatment with INH leads to deficiency of
A. Pyridoxine
B. Thiamine
C. Pantothenic acid
D. Niacin
Correct answer : A. Pyridoxine
INH increases urinary excretion of pyridoxine and impairs its utilisation. Hence prolonged treatment with INH leads to deficiency of Pyridoxine.
Which of the following agents is not associated with Hyperthermia
A. Amphetamines
B. MAO inhibitors
C. Atropine
D. Alcohol
Correct answer : D. Alcohol
Alcohol produces vasodilation (resulting in heat loss) and decreases heat production in the body. Hence it can cause hypothermia, not hyperthermia
All of the following statements about serotonin syndrome are true, except:
A. lt is not an idiosyncratic reaction
B. Can be caused by SSRI
C. Dantrolene is the drug of choice
D. Associated with hyperthermia and hypertension
Correct answer : C. Dantrolene is the drug of choice
Dantrolene is the drug of choice for malignant hyperthermia
Serotonin syndrome is a dose related phenomenon and is not idiosyncratic
It is treated with benzodiazepines, muscle relaxation, endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation
Dantrolene can be used in severe serotonin syndrome with malignant hyperthermia
Drug of choice in mild / moderate serotonin syndrome – cyproheptadine – an antihistaminic with antiserotonergic action
Which of the following drug is most commonly used world wide in maintenance doses for opioid dependence
A. Naltrexone
B. Methadone
C. lmipramine
D. Disulfiram
Correct answer : B. Methadone
Methadone is the most commonly used drug for treatment of opiod dependence.
Buprenorphine is also used.
Methadone is given as a once daily oral drug
It helps to prevent relapse, reduce craving and improve functioning
Which of the following movements will not be affected by involvement of the L5 Nerve root?
A. Thigh adduction
B. Knee Flexion
C. Knee Extension
D. Toe Extension
Answer : A. Thigh adduction
Thigh adduction is performed by adductor muscles (magnus, longus, brevis) with gracilis and pectineus acting as accessory muscles. None of them are supplied by L5 nerve root.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) differs from thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. In this reference the DIC is most likely characterized by:
A. Significant numbers of schistocytes
B. A brisk reticulocytosis
C. Decreased coagulation factor levels
D. Significant thrombocytopenia
Correct answer : C. Decreased coagulation factor levels
In DIC, the levels of coagulation factors are decreased. Whereas in TTP, coagulation factor levels are normal.
The usefulness of a ‘screening test` in a community depends on its :
A. Sensitivity
B. Specificity
C. Reliability
D. Predictive value
Correct answer : A. Sensitivity
A screening test should be sensitive to detect maximum possible cases. Specificity is not as important. After screening, we can apply a confirmatory test with high specificity.
If the grading of diabetes is classified as mild, moderate and severe the scale of measurement used is :
A. Interval
B. Nominal
C. Ordinal
D. Ratio
Correct answer : C. Ordinal
Here data can be arranged in a useful order. But there is no info regarding the size of each interval.
If prevalence of diabetes is 10%, the probability that three people selected at random from the population will have diabetes is:
A. 0.01
B. 0.03
C. 0.001
D. 0.003
Correct answer : C. 0.001
Prevalence of diabetes = 0.1
Probability that any one person selected from the population will have diabetes = 0.1
Probability that 3 people selected from the population will all have diabetes = 0.10.10.1 = 0.001
If the systolic blood pressure in a population has a mean of 130 mm Hg and a median of l40 mm Hg, the distribution is said to be?
A. Symmetrical
B. Positively skewed
C. Negatively skewed
D. Either positively or negatively skewed depending on the Standard deviation
Correct answer : C. Negatively skewed
Median is greater than mean. Hence it is negatively skewed.
You are here: Home » AIPGMEE » AIPGMEE 2004 » .
SPM – MCQ 132 – Standard deviation
lf each value of a given group of observations is multiplied by 10 the standard deviation of the resulting observations is :
A. Original std. Deviation x 10
B. Original std. Deviation /10
C. Original std. Deviation – l0
D. Original std. Deviation itself
Correct answer : A. Original std. Deviation x 10
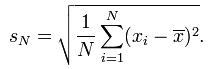
If we substitute 10x for x in the above formula, we can find that the SN (standard deviation of N values) will become 10 SN. (After squaring and finding square root).
Multi-purpose worker scheme in India was initiated following the recommendation of:
A. Srivastava Committee
B. Bhore Committee
C. Kartar Singh Committee
D. Mudaliar Committee
Correct answer : C. Kartar Singh Committee
Dietary changes advocated by WHO for prevention of heart diseases include all of the following except?
A. A decrease in complex carbohydrate consumption
B. Reduction in fat intake to 20-30 percent of caloric intake
C. Consumption of saturated fats be limited to less than 10% of total energy intake
D. Reduction of cholesterol to below l00mg per kcal per day
Correct answer : A. A decrease in complex carbohydrate consumption
WHO recommends an increase in consumption of complex carbohydrates.
“Five clean practices” under strategies for elimination of neonatal tetanus include all except :
A. Clean surface for delivery
B. Clean hand of the attendant
C. New blade for cutting the cord
D. Clean airway
Correct answer : D. Clean airway
The 5 clean practices are:
Clean hands
Clean delivery surface
Clean cord care
Clean blade for cutting cord
Clean cord tie and no application on cord stump
Essential component of RCH Programme in India include all of the following except:
A. Prevention and management of unwanted pregnancies
B. Maternal care including antenatal delivery & post-natal services
C. Reduce the under five mortality to half
D. Management of reproductive tract infections & sexually transmitted infections
Correct answer : C. Reduce the under five mortality to half
Sham rage is seen in
a) Decerebrate animals
b) Decorticate animals
c) Hypothalamic lesions
Thiazides are used in the treatment of all except?
A. CCF
B. Hyperlipidemia
C. Idiopathic hypercalceuria with nephrocalcinosis
D. ?
All are true about SACH – ic10 except?
A. SACH stands for Solid Ankle Cushion Heel
B. Shoes can be worn out
C. It has a woody heel
D. Managed by ?
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
Small vessels vasculitis seen in?
A. Giant cell arteritis
B. Microscopic Polyangitis
C. PAN
D. Takayasu arteritis
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
Age related dementia is associated with increase in which of the following amino acids ?
A.Homocysteine
B.Taurine
C.Glutamine
D. Methionine
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
Floxacin with the longest half-life ?
Please contribute to the discussion by helping us recall the question and by posting the correct answer.
Hypertriglyceridemia and Hypercholesterolemia seen in persons infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1; Treated with Protease Inhibitors.
Please contribute to the discussion by helping us recall the question and by posting the correct answer.
The National Population Policy of India has set the following goals except :
A. To bring down Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to replacement levels by 2015
B. To reduce the Infant Mortality Rate to 30 per l000 live births
C. To reduce the Maternal Mortality Rate to 100 per 100000 live births
D. 100 percent registration of births, deaths, marriages and pregnancies
Correct answer : A. To bring down Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to replacement levels by 2015
The goal of The National Population Policy of India is to bring down Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to replacement levels by 2010.
The following statements are true about Intrauterine devices (IUD) except:
A. Multiload Cu-375 is a third generation IUD
B. The pregnancy rate of Lippes loop and Cu—T 200 are similar
C. IUD can be used for Emergency Contraception within 5 days
D. Levonorgestrel releasing IUD has an effective life of 5 years.
Correct answer : A. Multiload Cu-375 is a third generation IUD
Multiload Cu-375 is a second generation IUD. Progestasert and Levonova are third generation IUCD’s.
The following statements about breast milk are true except :
A. The maximum milk output is seen at 12 months
B. The coefficient of uptake of iron in breast milk is 70%
C. Calcium absorption of human milk is better than that of cow’s milk
D. It provides about 65 kcals per 100 ml
Correct answer : A. The maximum milk output is seen at 12 months
The maximum milk output is seen at 5-6 months (730ml/day). At 12 months, it is only 525ml/day.
The current recommendation for breast feeding is that :
A. Exclusive breast-feeding should be continued till 6 months of age followed by supplementation with additional foods
B. Exclusive breast-feeding should be continued till 4 months of age followed by supplementation with additional foods
C. Colostrum is the most suitable food for a new born baby but it is best avoided in first 2 days
D. The baby should be allowed to breast—feed till one year of age
Correct answer : A. Exclusive breast-feeding should be continued till 6 months of age followed by supplementation with additional foods
A 10 month old child weighing 8kg has Bitot spots in both eyes. Which of the following is the most appropriate schedule to prescribe vitamin A to this child ?
A. 2 lakh units intramuscular (IM) on day 0, 14
B. 1 lakh units IM on day 0, 14
C. 2 lakh units IM on day 0, 1 and 14
D. 1 lakh units IM on day O, 1 and 14
Correct answer : D. 1 lakh units IM on day O, 1 and 14
WHO treatment schedule for active xerophthalmia:
– Medication given on day 0, 1 and 14
– Same dose on all 3 days
– Oral route preferred
– Age < 1year / any age with weight < 8kg - 50000 IU orally - Age > 1 year – 2 lakh IU orally / 1 lakh IU IM
Episodic muscular weakness is seen in all except?
A. Chanellopathy
B. Lambert eaton syndrome
C. Hypercalcemia
D. Hyperphosphatemia
Please contribute to the discussion by helping us recall the question and by posting the correct answer.
When to start kegels exercise?
A. After LSCS only
B. Immediately after delivery
C. 3rd trimester
D. After 3weeks of delivery
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
Identity of a rape victim is not to be revealed according to which section of the IPC ?
A.IPC 226
B.IPC 227
C.IPC 228
D.IPC 229
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
Cholera toxin acts via which of the following receptors?
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
An accident resulted in brain death in a patient. Which of the following is a sign of brain death?
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
Mitochondria is involved in all except?
A. Fatty acid synthesis
B. Chromosome
C. Fatty acid oxidation
D. Protein synthesis
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
A person is brought to casuality by police under the alleged offence of Sodomy. You being a medical officer are asked to examine the patient. Which will not be seen?
A. Presence of faecal smell
B. Presence of smegma
C. Frenual tear
D. Penile shaft constriction
Please contribute to the discussion by posting the correct answer with references and pointing out any errors in the question.
A neonate shows eroded skin (and more feature) while mother handles – diagnosis?
Please contribute to the discussion by recalling the question with options.
All of the following statements about leprosy are true except :
A. Multibacillary leprosy is diagnosed when there are more than 5 skin patches
B. New case detection rate is an indicator for incidence of leprosy
C. A defaulter is defined as a patient who has not taken treatment for 6 months or more
D. The target for elimination of leprosy is to reduce the prevalence to less than l per 10,000 population.
Correct answer : C. A defaulter is defined as a patient who has not taken treatment for 6 months or more
The term ‘defaulter’ is used in patients with tuberculosis. They are the ones who return with sputum smear positivity after leaving treatment for atleast 2 months.
All of the following are the mode of transmission of leprosy except?
A. Breast milk
B. Insect bite
C. Transplacental spread
D. Droplet infection
Correct answer : C. Transplacental spread
The following modes are proposed for transmission of leprosy:
Droplet infection
Contact spread – direct (skin to skin) and indirect (fomites)
Others (Breast milk, insect vectors, tattooing)
According to Intemational Health Regulations, there is no risk of spread of yellow Fever if the Aedes aegypti index remains below :
A. 1%
B. 5%
C. 8%
D. 10%
Correct answer : A. 1%
Aedes aegypti index is the percentage of houses and their premises in a limited well defined area that show actual breeding of aedes aegypti larvae. It should be kept below 1%. In addition to this, airports and seaports should be free of aedes aegypti breeding up to 400m from their perimeters.
The most appropriate test to assess the prevalence of tuberculosis infection in a community is :
A. Mass Miniature Radiotherapy
B. Sputum examination
C. Tuberculin Test
D. Clinical examination
Correct answer : C. Tuberculin Test
Tuberculin Test is the only test useful to assess the prevalence of tuberculosis in a community. Sputum examination is used to diagnose tuberculosis in an individual.
A 37 weeks pregnant woman attends an antenatal clinic at a Primary Health Centre. She has not had any antenatal visit till now. The best approach regarding tetanus immunization in this case would be to
A. Give a dose of Tetanus Toxoid (TT) and explain to her that it will not protect the new born and she should take the second dose after four weeks even if she delivers in the meantime
B. Do not waste the TT vaccine as it would anyhow be of no use in this pregnancy
C. Give one dose of TT and explain that it will not be useful for this pregnancy
D. Give her anti-tetanus Immunoglobulin along with the TT vaccine
Correct answer : A. Give a dose of Tetanus Toxoid (TT) and explain to her that it will not protect the new born and she should take the second dose after four weeks even if she delivers in the meantime
Tetans toxoid should be given to a pregnant women irrespective of the month of pregnancy. Second dose must be given atleast 4 weeks later. The newborn will not be protected unless 2 doses are taken. Newborns born to unimmunized mothers can be protected by giving tetanus antitoxin (750IU).
The following statements are true about DPT vaccine except:
A. Aluminium salt has an adjuvant effect
B. Whole killed bacteria of Bordetella pertussis has an adjuvant effect
C. Presence of acellular pertussis component increases its immunogenicity
D. Presence of H. influenzae type B component increases its immunogenicity
Correct answer : D. Presence of H. influenzae type B component increases its immunogenicity
Adjuvants increase the immunogenicity of a vaccine so that a lower quantity of antigen is enough to induce a sufficient antibody response. H.influenzae conjugate vaccine (PRP-D) is not useful for immunization against diphtheria. It does not increase immunogenicity of diphtheria.
A 3.5 year old child has not received primary immunization. Which of the following is the best vaccination advice to such a child?
A. BCG, DPT1 and OPV1. DPT2 and OPV2 after 4 weeks.
B. BCG, DT1, OPV1, measles, vitamin A
C. BCG, DPT1, OPV1, measles, vitamin A
D. DT1, DT2 and booster after 1 year
Correct answer : C. BCG, DPT1, OPV, measles, vitamin A
All of the following are used as proxy measures for incubation period except:
A. Latent period
B. Period of communicability
C. Serial interval
D. Generation time
Correct answer : B. Period of communicability
Period of communicability is the time period during which the person can transfer the infection to another person. It has no relation to the incubation period.
Latent period – Time period between disease onset and detection
Serial interval – Time period between onset of primary case and secondary case
Generation time – Time period between receipt of infection and maximal infectivity in a host
A study began in 1970 with a group of 5000 adults in Delhi who were asked about their alcohol consumption. The occurrence of cancer was studied in this group between 1990-1995. This is an example of :
A. Cross-sectional study
B. Retrospective cohort study
C. Concurrent cohort study
D. Case-control study
Correct answer : C. Concurrent cohort study
In a concurrent study (prospective study), the outcome under study has not yet occurred when the study starts. It requires long term follow up. Attrition is a big problem. It is an expensive study.
A 34-year old rickshaw puller has been using heroin for the past ten years. One evening his family members found him unconscious. He was brought to the casualty. On examination he had tachycardia, shallow breathing, constricted pupils. His blood pressure was 100/70 mm of Hg. He had brisk bilateral deep tendon reflexes. The planter reflexes were flexor on both sides. Which of the following is the best treatment for him?
A. Buprenorphine
B. Flumazenil
C. Methadone
D. Naloxone
Correct answer : D. Naloxone
The clinical features are suggestive of acute heroin intoxication. The drug of choice is naloxone – an opioid antagonist. It is reduces the action of heroin. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist. Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine antagonist. Methadone is used in rehabilitation of opoid addicts.
A 39 year old Carpenter has taken two bottles of liquor from the local shop. After about and hour, he develops confusion, vomiting and blurring of vision. He has been brought to the emergency department. He should be given
A. Naloxone
B. Diazepam
C. Flumazelnil
D. Ethyl alcohol
Correct answer : D. Ethyl alcohol
The clinical features are suggestive of methyl alcohol poisoning. Formic acid and formaldehyde (metabolites of methyl alcohol) are responsible for these symptoms. Ethyl alcohol is used for treatment as it saturates alcohol dehydrogenase, thereby decreasing production of formic acid and formaldehyde.
Which of the following is the most reliable method for estimating blood alcohol level?
A. Cavett’s test
B. Breath alcohol anaylzer
C. Gas liquid chromatography
D. Thin layer chromatography
Correct answer : C. Gas liquid chromatography
A middle aged man presents with paraesthesia of hand and feet. Examination reveals presence of ‘Mees’ lines in the nails and rain drop pigmentation in the hands; The most likely causative toxin for the above mentioned symptoms is :
A. Lead
B. Arsenic
C. Thallium
D. Mercury
Correct answer : B. Arsenic
‘Mees’ lines in the nails and rain drop pigmentation of skin are characteristic of arsenic poisoning. Treatment of choice – freshly precipitated hydrated ferric chloride.
A person was brought by police from the railway platform. He is talking irrelevant. He is having dry mouth with hot skin, dilated pupils, staggering gait and slurred speech. The most probable diagnosis is:
A. Alcohol intoxication
B. Carbamates poisoning
C. Organophosphorous poisoning
D. Dhatura poisoning
Correct answer : D. Dhatura poisoning
Features of dhatura poisoning: (All Datura plants contain tropane alkaloids such as scopolamine, hyoscyamine, and atropine)
Dilatation of pupils
Dryness of mouth
Difficulty in speech
Dysphagia
Dilatation of cutaneous blood vessels
Dry, hot skin
Drunken gait
Delirium
Drowsiness
Hydrogen peroxide is used in all of the following chemical tests for blood except:
A. Benzidine test
B. Phenophthalein test
C. Orthotolidine test
D. Teichmann’s test
Correct answer : D. Teichmann’s test
Benzidine test, phenolphthalein test, orthotolidine test and Leucomalachite green test utilise hydrogen peroxide to detect presence of blood. Hemoglobin present in blood is a peroxidase. It oxidises colourless bases to coloured salts in the presence of hydrogen peroxide.
Teichmann’s test (haemin crystal test) is done by converting haemoglobin to haemin crystals which is converted to salt in the presence of halogen and forms rhombic crystals.
Disputed maternity can be solved by using the following tests except?
A. Blood grouping
B. HLA typing
C. Preciptin test
D. DNA fingerprinting
Correct answer : C. Preciptin test
Preciptin test is used to differentiate human blood from animal blood.
Contre—coup injuries are seen in :
A. Brain
B. Diazepam
C. Flumazenil
D. Ethyl alcohol
Correct answer : A. Brain
In which of the following conditions, postmortem caloricity is seen?
A. Massive haemorrhage
B. Cyanide poisoning
C. Corrosive poisoning
D. Septicemia
Correct answer : D. Septicemia
Conditions causing postmortem caloricity:
Disturbance in heat regulation – sunstroke, pontine haemorrhage
Increased heat production in muscles – tetanus, strychnine poisoning
Bacterial / viral activity – septicemia / infections
Intense asphyxia
Deep blue colour of hypostasis is seen in death due to poisoning by
A. Potassium cyanide
B. Phosphorus
C. Aniline dyes
D. Carbon monoxide
Correct answer : C. Aniline dyes
Colour of post mortem lividity (hypostasis)
Normal – Bluish pink which later turns into bluish purple
Carbon monoxide – Bright cherry red
Cyanide – Pink
Phosphorous – Dark brown
Nitrates – Reddish brown
Chlorates – Chocolate brown
Hydrogen sulphide – Bluish Green
Aniline – Deep blue
Opiates – Black
A 25 year old person sustained injury in right eye. He developed right comeal opacity following the injury. Left eye was already having poor vision. Corneoplasty of right eye was done and vision was restored. Medicolegally such injury is labelled as :
A. Grievous
B. Simple
C. Dangerous
D. Serious
Correct answer : A. Grievous
Injuries classified as Grievous by Section 320 of IPC:
Emasculation
Permanent privation of the sight of either eye
Permanent privation of the hearing of either ear
Privation of any member or joint
Destruction or permanent impairing of the powers of any member or joint
Permanent disfiguration of the head or face
Fracture or dislocation of a bone or tooth
Any hurt which endangers life or which causes the sufferer to be during the space of twenty days in severe bodily pain, or unable to follow his ordinary pursuits
The cephalic index of Indian population is between:
A. 70-75
B. 75-80
C. 80-85
D. 85-90
Correct answer : A. 70-75
Cephalic index in different races:
Negroes, Aryans, Aborigines – 70-75
Europeans – 75-80
Mongols, Native americans, Oriental Asians – 80-85
A convict whose family or relations were not known and no biological sample was available with jail authorities, escaped from the jail. A dead body resembling the convict was found in nearby forest. but due to mutilation of face, identity could not be established. The positive identity that he is the same convict who escaped from jail can be established by
A. Blood Grouping
B. DNA Profile
C. Anthropometry
D. HLA typing
Correct answer : C. Anthropometry
Blood grouping, DNA profiling and HLA typing require a biological sample.
BAL is useful in treating poisoning due to all except?
A. Lead
B. Organic mercury
C. Cadmium
D. Arsenic
Correct answer : C. Cadmium
Complexes formed by combining cadmium / iron with BAL are toxic. Hence BAL (dimercaprol) is contraindicated in treatment of iron / cadmium poisoning.
Which of the following statements is not true about Tacrolimus?
A. It is macrolide Antibiotic
B. lt is indicated for the prophylaxis of organ transplant rejection
C. Glucose intolerance is a well Recognized side effect
D. It can be safely administered with any Nephrotoxic drug
Correct answer : D. It can be safely administered with any Nephrotoxic drug
Tacrolimus is nephrotoxic and hence cannot be administered safely with other nephrotoxic drugs.
Clinically significant drug interaction occurs between pyridoxine and all the following drugs except?
A. Isoniazid
B. Cyclosporine
C. Levodopa
D. Hydralazine
Correct answer : B. Cyclosporine
Pyridoxine – drug interactions :
INH – induces a pyridoxine deficiency state
Levodopa – pyridoxine promotes peripheral conversion of levodopa to dopamine – thus it decreases therapeutic action of levodopa in the brain
Oral contraceptive pills – decrease pyridoxine levels in some females
Hydralazine – impairment of pyridoxine utilisation
4-deoxy pyridoxine – pyridoxine antagonist
Which is the most active single chemotherapeutic agent in the treatment of Leiomyosarcoma?
A. Adriamycin
B. Doxorubicin
C. Methotrexate
D. Cisplatin
Correct answer : A. Adriamycin / B. Doxorubicin
Adriamycin (brand name of doxorubicin) is very useful in the treatment of leiomyosarcoma.
All of the following are hormonal agents used against breast cancer except?
A. Letrozole
B. Exemestane
C. Taxol
D. Tamoxifen
Correct answer : C. Taxol
Taxol (paclitaxel) is a chemotherapeutic agent classified under antimicrotubule agents.
Hormonal agents used against breast cancer:
Aromatase inhibitors (letrozole, anastrazole)
Aromatase inactivators (exenestase)
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (Tamoxifen)
Patients suffering from multidrug resistant tuberculosis can be treated with all the following drugs except:
A. Tobramycin
B. Amikacin
C. Ciprofloxacin
D. Clarithromycin
Correct answer : A. Tobramycin
Second line drugs for treatment of tuberculosis:
PAS
Ethionamide
Kanamycin
Amikacin
Capreomycin
Thiocetazone
Cycloserine
Ciprofloxacin
Ofloxacin
Rifabutin
Clarithromycin
Azithromycin
A 30 year old pregnant woman developes tuberculosis. Which of the following antitubercular drugs should not be used:
A. INH
B. Rifampicin
C. Streptomycin
D. Ethambutol
Correct answer : C. Streptomycin
Streptomycin is contraindicated in pregnant women because of fetal ototoxicity.
Which of the following Antimicrobials has Antipseudomonal action:
A. Cefopodoxime proxetil
B. Ceforanide
C. Cefotetan
D. Cefoperazone
Correct answer : D. Cefoperazone
Cephalosporins with antipseudomonal action:
Cefoperazone
Ceftazidime
Other 3rd generation cephalosporins (not reliable)
Which of the following fluoroquinolones does not require dose adjustment in a patient with creatinine clearance of < 50mg/min?
A. Ciprofloxacin
B. Trovafloxacin
C. Lomefloxacin
D. Sparfloxacin
Correct answer : B. Trovafloxacin
Fluoroquinolones that are excreted mainly by non renal mechanisms:
Pefloxacin
Trovafloxacin
Grepofloxacin
Nalidixic acid
A post operative patient developed septicemia and was empirically started on combination chemotherapy by a new resident doctor. However, when the patient did not respond even after 10 days of antibiotics treatment, the review of the charts was done. It was found that the resident doctor had started the combination of antibiotics which was mutually antagonistic in action. Which one of the following is the most likely
combination that was given?
A. Vancomycin and Amikacin
B. Cephalexin and Gentamicin
C. Ampicillin and Chloramphenicol
D. Ciprofloxacin and Piperacillin
Correct answer : C. Ampicillin and Chloramphenicol
When a Bactericidal agent is given along with a Bacteriostatic agent, 2 outcomes are possible.
Synergism – when the bacteria has low sensitivity to the cidal agent
Antagonism – when the bacteria has high sensitivity to the cidal agent
Bactericidal drugs:
Beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins (cephems), monobactams, and carbapenems)
Vancomycin
Daptomycin
Fluoroquinolones
Metronidazole
Nitrofurantoin
Co-trimoxazole
Telithromycin
Aminoglycosides
Bacteriostatic drugs:
Tetracyclines
sulfonamides
Spectinomycin
Trimethoprim
Chloramphenicol
Macrolides
Lincosamides
Which of the following statements is not true regarding sulfonamides:
A. Sulfasalazine is absorbed well from GIT
B. Crystalluria can occur with sulfonamide administration
C. Sulfonamide administration to Newborn may cause Kernicterus
D. Sulfonamides are of value in treatment of infections due to Norcardia species
Correct answer : A. Sulfasalazine is absorbed well from GIT
Sulfasalazine is poorly absorbed (10-20%) from the GIT .
Morphine can be used in all the following conditions except:
A. Head injury
B. Asthma
C. Hypothyroidism
D. Diabetes
Correct answer : A. Head injury
Morphine is contraindicated in head injury for the following reasons:
Causes carbondioxide retention – this in turn increases intracranial tension
Therapeutic doses can cause respiratory depression in head injury patients
Vomiting, miosis and altered mentation caused by morphine can interfere with assessment of neurological status
Morphine should be avoided in those with bronchial asthma as it can precipitate an attack of asthma. But it is not contraindicated. Patients with hypothyroidism are more sensitive to the effects of morphine.
Which of the following action is ascribed to delta type of opioid receptors?
A. Supraspinal analgesis
B. Respiratory depression
C. Euphoria
D. Reduced intestinal motility
Correct answer : A. Supraspinal analgesis
Functions of delta type opioid receptors are:
supraspinal analgesia
spinal analgesia
modulation of hormone and neurotransmitter release
The protective effects of breast milk are known to be associated with:
A. IgM antibodies
B. Lysozyme
C. Mast cells
D. IgA antibodies
Correct answer : D. IgA antibodies
Although breast milk contains both breast milk and antibodies; antibodies play the major role in providing immunity. Breast fed babies have lower incidence of diarrhoea, otitis media, pneumonia, bacteremia and meningitis.
In a case of Dysgerminoma of ovary one of the following tumor markers is likely to be raised.
A. Serum HCG
B. Serum alphafetoprotein
C. Serum lactate dehydrogenase
D. Serum inhibin
Correct answer : C. Serum lactate dehydrogenase
Dysgerminomas produce placental alkaline phosphatase and lactate dehydrogenase. Pure dysgerminomas do not produce AFP and HCG.
Most common nerve injured in supracondylar fracture humerus?
A. Median
B. Radial
C. Ulnar
D. Anterior interosseous nerve
Correct answer : D. Anterior interosseous nerve
In order studies, the radial nerve was found to be the one most commonly injured. But recent studies have shown that the median nerve, particularly the anterior interosseous branch is the most commonly damaged in supracondylar fracture of humerus.
Orthotolidine test is used for detecting:
A. Chlorine
B. Nitrites
C. Nitrates
D. Ammonia
Correct answer : A. Chlorine
Vitamin K is involved in the post translational modification of?
A. Glutamate
B. Aspartate
C. Proline
D. Lysine
Correct answer : A. Glutamate
Vitamin K is involved in the gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid residues.
False about pneumococcus is?
A. Capsule aids in virulence
B. Commonest cause of otitis media and pneumonia
C. Meningitis caused by it is milder than by other organisms
D. Bile sensitive
Correct answer : C. Meningitis caused by it is milder than by other organisms
Pneumococcal meningitis is a very serious condition.
Which among the following is a cardioprotective fatty acid?
A. Palmitic acid
B. Stearic acid
C. Oleic acid
D. Omega-3 fatty acids
Correct answer : Both C and D
Palmitic acid and stearic acid are saturated fatty acids – promote atherogenesis.
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid – cardioprotective, reduce LDL.
Omega-3 fatty acids like linolenic acid and docosahexaenoic acid are cardioprotective.
All India PG Entrance Examination (AIPGMEE) 2012 will be conducted on 8th January 2012. The exam is conducted by the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS). Applications are accepted only via online submission at www.aiimsexams.org. The candidates should complete the required period of 12 months pre-registration internship from a recognized Hospital on or before 31st March, 2012. The prospectus is available on the website www.aiimsexams.org and must be read by the applicants before applying. The cost of online Application-cum-Examination fee is Rs.1000/- (Rs.800/- in case of SC/ST candidates).Last Date for submission of On-line applications and closing of Registration – 21.12.2011 (up to 5:00 PM)
Drug implicated for prolonging QT interval in a premature baby is :
A. Domperidone
B. Metoclopramide
C. Cisapride
D. Omeprazole
Correct answer : C. Cisapride
Cisapride can cause QT prolongation when administered along with drugs like ketoconazole which inhibit hepatic cytochrome p-450 CYP 3A4 enzyme.
All the following statements regarding interactions of levodopa are correct except:
A. In Parkinsonism, phenothiazines reduce its efficacy
B. It is a prodrug
C. Pyridoxine reduces effect of levodopa in parkinsonism
D. Domperidone blocks levodopa induced emesis and its therapeutic potential
Correct answer : D. Domperidone blocks levodopa induced emesis and its therapeutic potential
Domperidone blocks the emesis induced by levodopa. It has no affect on the therapeutic potential.
A patient of peptic ulcer was prescribed ranitidine and sucralfate in the morning hours. Why is this combination incorrect:
A. Ranitidine combines with sucralfate and prevents its action
B. Combination of these two drugs produces serious side effects like agranulacytosis
C. Ranitidine decreases the gastric pH so sucralfate is not able to act
D. Sucralfate inhibits absorption of ranitidine
Correct answer : D. Sucralfate inhibits absorption of ranitidine
Ranitidine can increase the gastric pH and prevent polymerization (occurs at a pH < 4) of sucralfate.
Sucralfate decreases the absorption of many drugs including ranitidine.
Which of the following is not an adverse effect of chronic amiodarone therapy?
A. Pulmonary fibrosis
B. Hypothyroidism
C. Hyperthyroidism
D. Systemic lupus erythematosus
Correct answer : D. Systemic lupus erythematosus
Adverse effects of amiodarone:
-Thyroid function abnormality – hyperthyroidism / hypothyroidism
-Cardiac depression
-Pulmonary alveolitis and fibrosis
-Peripheral neuropathy
-Corneal micro deposits
-Photosensitivity
A 60 year old man with rheumatic mitral stenosis with atrial fibrillation is on therapy for a fast ventricular rate. While on treatment, he developed a regular pulse of 64/min. The most likely drug being administered was:
A. Verapamil
B. Digoxin
C. Carvedilol
D. Propranolol
Correct answer : B. Digoxin
Slow ventricular rate in a patient with atrial fibrilliation indicates complete heart block – a complication of digoxin therapy.
Auto-Rikshaw ran over a child’s thigh, there is a mark of the tyre tracks, it is an
A. Contact bruise
B. Patterned bruise
C. Imprint abrasion
D. Ectopic bruise
Correct answer: C. Imprint abrasion
Imprint abrasions, also known as Impact Abrasions are caused by the stamping of some object against the skin like radiators of cars in vehicular accidents.
Which of the following does not bind to GABA receptor chloride channels?
A. Ethanol
B. Alfaxalone
C. Zolpidem
D. Buspirone
Correct answer : D. Buspirone
All of the following are advantages of using Raloxifene over estrogen in post menopasual women except?
A. Reduces fracture rates
B. Avoids Endometrial hyperplasia
C. Reduces incidence of venous thrombosis
D. No increase in incidence of breast carcinomas
Correct answer : C. Reduces incidence of venous thrombosis
Intake of raloxifene results in 3 fold increase in risk of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
All of the following Anticancer agents cause bone marrow depression except?
A. Chlorambucil
B. Daunorubicin
C. Doxorubicin
D. Flutamide
Correct answer : D. Flutamide
Side effects of flutamide are gynaecomastia, breast tenderness, liver damage, nausea and hot flushes. It has anti androgenic action.
All of the following statements about an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor are true except:
A. Reduces intestinal absorbtion of carbohydrates
B. Effective in both type l & 2 diabetes
C. Hypoglycemia is a common & serious side effect
D. Can be used with other oral Hypoglycemic drugs
Correct answer : C. Hypoglycemia is a common & serious side effect
Important side effects of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors – flatulence, diarrhoea, abdominal pain. They arise due to presence of undigested carbohydrates in the colon which get fermented to short chain fatty acids with gas production.
Which one of the following statements about biguanides is not true?
A. Don’t stimulate insulin Release
B. Decrease hepatic glucose production
C. Renal Dysfunction is not a contraindication for their use
D. Can be combined with sulfonylureas
Correct answer : C. Renal Dysfunction is not a contraindication for their use
Biguanides are contraindicated in renal disease, hepatic disease and conditions causing tissue anoxia due to increased risk of lactic acidosis.
Sympathomimetic drugs are useful in the therapy of all of the following conditions except?
A. Acute decompensated heart failure
B. Hypotension
C. Hypertension
D. Erectile dysfunction
Correct answer : D. Erectile dysfunction
Erection is mediated by parasympathetic nervous system.
In which of the following phases of clinical trial of drug, ethical clearance is not required?
A. Phase I
B. Phase II
C. Phase III
D. Phase IV
Correct answer : D. Phase IV
Phase IV (post marketing surveillance) does not need any ethical clearance.
All are true about pheochromocytoma except?
A. 90% are malignant
B. 95% occur in the abdomen
C. They secrete catecholamines
D. They arise from sympathetic ganglions
Correct answer : A. 90% are malignant
Approximately 10% of pheochromocytomas are malignant.
A highly ionized drug :
A. Is excreted mainly by the kidneys
B. Corsses the placental barrier easily
C. Is well absorbed from the intestine
D. Is highly protein bound
Correct answer : A. Is excreted mainly by the kidneys
Highly ionized drugs are lipid insoluble. Hence they are poorly absorbed by the intestine. They cannot cross the placental barrier easily. And since they are not reabsorbed in the renal tubules, they are excreted in urine.
Which of the following statements is true regarding ARBO viruses :
A. Yellow fever is endemic in India
B. Dengue virus has only one serotype
C. Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD) is transmitted by ticks
D. Mosquito of culex vishnui complex is the vector of Dengue fever
Correct answer : C. Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD) is transmitted by ticks
Yellow fever is not present in India
Dengue virus has 4 serotypes.
Dengue fever is transmitted by aedes mosquito.
A young pregnant woman presents with fulminant hepatic failure. The most likely aetiological agent is:
A. Hepatitis B virus
B. Hepatitis C virus
C. Hepatitis E virus
D. Hepatitis A virus
Correct answer : C. Hepatitis E virus
Hepatits E causes fulminant hepatic failure in 1-2% of cases (20% in pregnancy).
All of the following clinical features are associated with Enteroviruses except :
A. Myocarditis
B. Pleurodynia
C. Herpangina
D. Hemorrhagic fever
Correct answer : D. Hemorrhagic fever
Hemorrhagic fever is caused by hantavirus.
All of the following statements are true regarding poliovirus except :
A. It is transmitted by feco-oral route
B. Asymptomatic infections are common in children
C. There is a single serotype causing infection
D. Live attenuated vaccine produces herd immunity
Correct answer : C. There is a single serotype causing infection
Polio virus has 3 serotypes.
Laboratory diagnosis of viral respiratory tract infections can be established by all of the following tests except :
A. Detection of virus specific IgM antibodies in single serum specimen
B. Demonstration of viral antigens by indirect immunofluorescence assay in nasopharyngeal washings
C. Isolation of viruses using centrifugation enchanced culture
D. Detection of viral heamagglutination inhibiting (HAI) antibodies in a single serum specimen
Correct answer : D. Detection of viral heamagglutination inhibiting (HAI) antibodies in a single serum specimen
For diagnosis of viral infection, it is necessary to demonstrate viral heamagglutination inhibiting (HAI) antibodies in at least 2 serum specimens.
Which is not an autoimmune disease?
A. SLE
B. Grave’s disease
C. Myasthenia gravis
D. Sickle cell disease
Correct answer : D. Sickle cell disease
Denominator in Maternal Mortality Rate?
A. Total number of live births
B. Total number of married women
C. Total number of births
D. Midyear population
Correct answer : A. Total number of live births
Ova albumin antigen was injected into a rabbit. What is the first antibody produced against it?
A. IgG
B. IgM
C. IgE
D. IgD
Correct answer : IgM
Epstein Barr (EB) virus has been implicated in the following malignancies except:
A. Hodgkin‘s disease
B. Non Hodgkin‘s lymphoma
C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
D. Multiple myeloma
Correct answer : D. Multiple myeloma
Epstein Barr (EB) virus associated conditions:
Infectious mononucleosis
Acute transverse myelitis
Guillain Barre syndrome
Aplastic anemia
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Peripheral neuritis
T cell lymphoma
Burkitt’s lymphoma
Hodgkin’s disease
CNS lymphoma
Lymphoproliferative syndrome
Gastric carcinoma
Leiomyosarcoma
Tonsillar carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Thymoma
Oral hairy leukoplakia (in adults with HIV)
The most sensitive method for detecting cervical Chlamydia trachomatis infection is:
A. Direct fluorescent antibody test
B. Enzyme immunoassay
C. Polymerase chain reaction
D. Culture on irradiated McConkey cells
Correct answer : C. Polymerase chain reaction
Ligase chain reaction and Polymerase chain reaction are the most sensitive methods for detection of chlamydia.
A 20 years old male patient presents to the STD clinic with a genital ulcer. The gram stain of the smear from ulcer shows gram negative coccobacilli. The most appropriate media for culture would be:
A. Thayer Martin Medium
B. Blood agar with X & V factors
C. Chocolate agar with IsoVitaleX
D. Teilurite blood agar
Correct answer : C. Chocolate agar with IsoVitaleX
The clinical picture is suggestive of soft sore (chancroid) caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. Chocolate agar with IsoVitaleX is used for its culture.
Other culture media:
Thayer Martin Medium – Gonococci
Blood agar with X & V factors – Haemophilus influenzae
Tellurite blood agar – Corynbacterium diphtheriae
A 30 year old woman with a bad obstetric history presents with fever. The blood culture from the patient grows gram—positive small to medium coccobacilli that are pleomorphic, occurring in short chains. Direct wet mount from the culture shows tumbling motility. The most likely organism is:
A. Listera monocytogenes
B. Corynebacterium sp.
C. Enterococcus sp.
D. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Correct answer: A. Listera monocytogenes
Listeria are small gram positive coccobacilli with characteristic tumbling motility. They are non motile at 38 degree Celsius as the flagellae are produced optimally at 20-30 degree Celsius.
Regarding gas gangrene one of the following is correct:
A. It is due to Clostridium Botulinum infection
B. Clostridial species are gram—negative spore forming anaerobes
C. The clinical featues are due to the release of protein endotoxin
D. Gas is invariably present in the muscle compartments
Correct answer : D. Gas is invariably present in the muscle compartments
Clostridia species are the most important agents responsible for gas gangrene. But Clostridium botilinum does not cause gangrene. Clostridia are gram positive spore forming anaerobes. Clinical features are due to release of exotoxin.
A farmer presenting with fever off-and on for the past 4 years was diagnosed to be suffering from chronic brucellosis. All of the following serological tests would be helpful in the diagnosis at this state except:
A. Standard Agglutination test
B. 2 Mercapto-ethanol test
C. Complement fixation test
D. Coomb‘ s test
Correct answer : A. Standard Agglutination test
Standard agglutination is mainly useful for identification of IgM antibodies. But in chronic brucellosis (and other chronic infections), the IgM levels will be very low. IgG will be predominant. Hence it is not useful in diagnosing chronic brucellosis.
A man, after skinning a dead animal, developed a pustule on his hand. A smear prepared from the lesion showed the presence of Gram positive bacilli in long chains which were positive for McFadyean’s reaction. The most likely aetiological agent is :
A. Clostridium tetani
B. Listeria monocytogenes
C. Bacillus anthracis
D. Actinamyces sp
Correct answer : C. Bacillus anthracis
The history (animal contact), clinical picture (pustule in the area of contact) and lab findings (gram positive bacilli in chains with McFadyean reaction positive) are all characteristic of infection by Bacillus anthracis.
Toxins are implicated as the major pathogenetic mechanism in all of the following bacterial diarrhoeas except?
A. Vibrio cholerae
B. Shigella sp.
C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus
D. Staphylococcus aureus
Correct answer : C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Vibrio parahaemolyticus causes enteritis by invasion of intestinal epithelium.
A microbiologist wants to develop a vaccine for prevention of attachment of diarrhoeagenic E. coli to the specific receptors in the gastro-intestinal tract. All of the following fimbrial adhesions would be appropriate vaccine candidates except :
A. CFA-l
B. P-Pili
C. CS—2
D. K 88
Correct answer : B. P-Pili
P-Pili are involved in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. It binds to the P blood group substance on erythrocytes and uroepithelial cells. They have no role in gastrointestinal infection.
Which of the following toxins acts by inhibiting protein synthesis
A. Cholera toxin
B. Shiga toxin
C. Pertussis toxin
D. LT of enterotoxigenic E.coli
Correct answer : B. Shiga toxin
Other toxins which inhibit protein synthesis:
-Diphtheria toxin
-Pseudomonas toxin
A 20 year old man presented with hemorrhagic colitis. The stool sample grew Escherichia coli in pure culture. The following serotype of E.coli is likely to be the causative agent :
A. O l57:H7
B. O 159:H7
C. O 107:H7
D. O 55:H7
Correct answer : A. O l57:H7
True regarding obstructive azoospermia is?
A. Increased FSH and LH
B. Increased FSH and normal LH
C. Normal FSH and increased LH
D. Normal FSH and LH
Correct answer : D. Normal FSH and LH